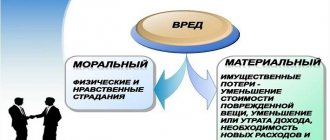
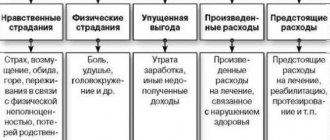
What is moral harm
The concept of moral harm is given by Article 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It is understood as a violation of the non-property rights of citizens, which may manifest itself in physical or moral suffering of a person or his loved ones.
The following situations may serve as examples of causing moral harm:
Additionally
Another basis for obtaining compensation is violation of consumer rights. Compensation for moral damage to the consumer in case of violation of his rights is carried out in cases of receiving a low-quality product or service, concealing additional information about them, non-compliance with the terms of the contract or failure to provide instructions (as a result of which the goods were damaged), provided that this affected the moral state of the victim.
- Causing harm to the health or life of a person (for example, injury received as a result of an accident; murder of a close relative, etc.). How to receive compensation for moral damages in an accident, read here;
- Unlawful deprivation of liberty (keeping a person in custody without legal grounds);
- Insult;
- Slander, humiliation of honor, dignity, business reputation of a person (when compensating for damage and establishing its amount in this situation, the circle of people who received false information is of great importance: 1-2 people - during an oral conversation, 100 or more - when publishing information in the media );
- Interference with privacy;
- Disclosure of secrets protected by law (for example, adoption or medical confidentiality);
- Infringement of copyright or other personal rights.
It is these cases that most often become grounds for compensation for moral damage in practice. The general grounds for compensation are listed in Article 1100 of the Civil Code. However, it should be borne in mind that there is no clear list of such grounds. Every person experiencing moral suffering has the right to demand compensation in material terms from the person responsible for causing this suffering.
Another comment on Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
1. Contrary to the title of the comment. Art., it deals with the form and amount of compensation for moral damage.
In contrast to the previously existing rule on the admissibility of various material forms of compensation for moral damage (Article 131 of the Fundamentals of Civil Legislation), paragraph 1 comment. Art. contains a mandatory rule on monetary compensation, which cannot be changed either by agreement of the parties or by the court. From the point of view of common sense, the current norm is hardly justified and justified. Why the offender cannot be obliged to compensate for moral damage in a different, non-monetary material form, when this is more in the interests of the victim, or even more so of both parties, remains completely unclear.
2. If no agreement is reached between the parties on the issue of the amount of compensation for moral damage, this amount is determined by the court. In paragraph 2 of the comment. Art. contains criteria for determining the amount of compensation that the court must follow. These are the nature of the physical and moral suffering inflicted on the victim, the individual characteristics of the victim, the degree of guilt of the harm-doer, the requirements of reasonableness and justice.
Additional rules for assessing moral damage were developed by the Plenum of the Supreme Court, according to the explanations of which the amount of compensation for moral damage cannot be made dependent on the size of the satisfied claim for compensation for material harm, losses and other material claims. When determining the amount of compensation for moral damage, you should also find out the victim’s opinion regarding the amount of compensation (clause 1, 8 of the Supreme Court Resolution No. 10).
Amount of compensation for moral damage
The possibility of compensation for moral damage is enshrined in Article 1099 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure and amount of compensation is regulated by Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Moral damage is always compensated in monetary terms. In order to receive compensation, a person must go to court, since it is this body, in accordance with Article 1101 of the Civil Code, that has the right to determine the grounds and amount of compensation.
It is worth noting: the victim has the right to demand compensation for moral damage both simultaneously with the main claims (that is, in a claim for insult, slander, etc.), and by filing a separate statement of claim with the court for compensation for moral damage.
When determining the amount of compensation for moral damage, the court takes into account:
- How much suffering the victim suffered (for example, based on judicial practice, it is believed that when losing a close relative, the greatest moral suffering occurs if the death occurred in front of loved ones);
- How much the defendant is to blame for causing harm (first of all, the degree of guilt is assessed: negligence, direct or indirect intent);
- Individual characteristics of the victim’s life and health, which could affect his emotional perception of the situation (for example, the victim’s pregnancy, increased excitability as a result of illness, etc.);
- Consequences of harm (for example, disability as a result of injury, family breakdown due to the dissemination of slanderous information, etc.);
- The financial condition of the defendant.
It should also be noted that compensation for property damage, if any, does not prevent the defendant from demanding compensation for moral damage from the perpetrator.
What is moral damage and how to get compensation for it can be seen in the video below
Commentary on Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
1. In Art. 1101 provides that moral damage is compensated in monetary form. At the same time, citizens who independently exercise their civil rights have the right to consent to the defendant’s proposal for compensation for moral damage in kind, by providing certain goods or services
2. The amount of compensation for moral damage in monetary form is determined by the court on the basis of the specific circumstances of the dispute, taking into account the evidence presented by the plaintiff about the nature of the physical and moral suffering caused. The court also takes into account the degree of guilt of the harm-doer, his property status, circumstances related to the guilty behavior of the victim himself, and other information. The principle of reasonableness and justice, named in paragraph 2 of Art. 1101, is the most important criterion for the court to determine the amount of compensation for moral damage.
Types of claims for moral damages
- Infringement of copyright (a case of a non-property nature) – Article 1251 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Infringement of rights in the sphere of labor activity – Art. 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Actions or inactions on the part of the employer that go beyond the corporate culture. The subject of such violations are hired employees. Legislative basis – Art. 237 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Removal from a position without sufficient reasons or transfer to another position without agreement with the employee - Art. 394 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Violation of secrecy in matters of will – Article 1123 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Article 5 of the Law “On Consumer Protection” applies to producers of goods and services;
- Unlawful situations arising as a result of the distribution of advertising materials are regulated within the framework of the Law “On Advertising”, adopted on March 13, 2006;
- Offenses in the field of tourism against clients by tour operators and travel agents are considered on the basis of the Federal Law of November 24, 2006 “On the fundamentals of tourism activities in Russia”;
- Disclosure of personal information or dishonest use of personal information;
- Other.
Expert opinion
Orlov Denis Ignatievich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in drafting contracts.
Moral harm is based on moral suffering. Moral suffering refers to feelings that express general psycho-emotional discomfort, a feeling of depression, constant pressure and tension.
What amount is claimed in claims for compensation for moral damage, review of judicial practice?
In accordance with the requirement of Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the amount of the penalty, the court is guided by the principle of reasonableness and fairness. These principles are evaluative in nature, and the plaintiff, defendant and court interpret them differently.
Expert opinion
Orlov Denis Ignatievich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specialization: family law. Has experience in drafting contracts.
Therefore, as judicial practice on compensation for moral damage in a civil case shows, it is quite difficult to obtain the amount of compensation claimed by the plaintiff. When making a decision, the court, as a rule, reduces it by 3 or even 10 times.
The greatest compensation can be achieved if, in addition to moral suffering, the person received bodily injuries.
You should be aware that the legislation does not contain the size of the maximum amount of recovery, as well as the procedure for calculating it.
Moral damage in case of an accident
You can learn about the recovery of moral damages if you are involved in an accident in this video:
Drivers with MTPL or CASCO insurance policies can count on compensation for damage caused to their property during an accident. However, compensation for damage to health and moral harm is not included in the terms of this type of insurance.
In such cases, compensation for damage to health, that is, compensation for the costs of treatment, prosthetics, surgery, rehabilitation, restorative procedures, purchase of medications, is included in the concept of compensation for material damage. And documents confirming such costs serve as the basis for recovery.
For this reason, courts, as a rule, satisfy claims in full. That is, if there are documents confirming:
- fact of an accident;
- the defendant's guilt in it;
- harm to health, in the form of bodily injury;
- restoration costs.
Both material costs and moral damage can be fully compensated. If there is no damage to health, then the court, when considering a civil case, compensates for moral suffering for property damaged by the accident, but in a smaller amount.
Moral damage in case of violation of consumer rights
The possibility of recovering moral damages in a civil case in case of violation of consumer rights is provided for in Article 15 of the Federal Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”. When recovering, the plaintiff must prove the guilt of either the seller, or the manufacturer or importer.
As a rule, evidence of guilt is the conclusion of experts who establish the fact of violation of consumer rights. The law provides for compensation for moral damage in a civil case, regardless of property damage and losses incurred by the person.
Moral damage in case of violation of labor rights
Compensation for moral damage in labor relations is discussed in this video:
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a definition of the concept of moral harm caused to an employee. However, in judicial practice, compensation for moral damage from employers in addition to the material damage caused is quite common.
The courts, as a rule, always satisfy the employee’s demands, but in a smaller amount than stated in the claim. When making a decision, the justice body is guided by Article 21 of the Labor Code, which grants the employee the right to compensation for moral damage, as well as the rules of law:
- prohibiting discrimination in the labor sphere.
- providing for liability to compensate for moral damage in a civil case in case of non-payment of wages.
- establishing the employer's liability in the event of illegal dismissal or transfer to another job.
The amount of compensation can be established by the parties, or can be determined by the judge when considering the case. Evidence of infliction of moral suffering is the establishment of a violation of the employee’s labor rights.
Moral damage when causing harm to health
When calculating compensation for moral damage in the event of personal injury, when considering a civil case in court, the degree of guilt of the defendant and the severity of the damage are taken into account. Health damage is divided into three types:
- mild degree:
- moderate;
- serious harm to health.
The degree of damage to health is established by experts, and when establishing the amount of compensation, the presence of irreversible consequences, time spent on treatment, and loss of ability to work are taken into account.
Moral damages for slander and insults
How the law punishes personal insult is discussed in this video:
Damages for defamation can be recovered if there is a court verdict accusing a person of a crime under Art. 128.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In such cases, such a verdict serves as actual evidence of harm caused by the dissemination of deliberately false information that discredits the honor, dignity or business reputation of a person.
Recovery of moral damages for insult is also possible if it is possible to bring the offender to justice under Art. 5.61 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
However, the “Review of the practice of courts considering cases on disputes regarding the protection of honor, dignity and business reputation,” approved by the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in 2020, states that the courts unlawfully refuse to compensate plaintiffs for damages for insult.
My own lawyer
Official text: Article 1100. Grounds for compensation for moral damage Compensation for moral damage is carried out regardless of the guilt of the harm-doer in cases where: - harm was caused to the life or health of a citizen by a source of increased danger;
- harm was caused to a citizen as a result of his illegal conviction, illegal prosecution, illegal use of detention or a written undertaking not to leave as a preventive measure, illegal imposition of an administrative penalty in the form of arrest or correctional labor; - harm was caused by the dissemination of information discrediting honor, dignity and business reputation; - in other cases provided by law. Lawyer's comment: Article 131 of the Fundamentals of Civil Legislation, which was applied before the entry into force of part two of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, established that moral damage is compensated if the causer is at fault. The provision on guilt as one of the mandatory conditions for the onset of liability for causing moral harm is retained in Article 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The Plenum of the RF Supreme Court in Resolution No. 10 clarified that exceptions to this general rule must be expressly provided for by law. Article 1100 provides for three cases when compensation for moral damage is carried out regardless of the guilt of the perpetrator, allowing for the possibility of expanding this list. Without guilt, liability for causing moral harm by illegal actions of the bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation, prosecutor's office and court (Article 1070 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) is limited to cases of illegal conviction, illegal prosecution, illegal use of detention or a written undertaking not to leave as a preventive measure. , illegal imposition of an administrative penalty in the form of arrest or correctional labor. Moral damage caused, for example, by actions such as illegal detention of a suspect in a crime, search, removal from office, are compensated in the presence of guilt of the preliminary investigation bodies, the prosecutor's office and the court on the grounds established by paragraph 2 of Article 1070. The novelty was the inclusion of cases without guilty liability for causing moral harm and attacks on honor, dignity and business reputation. But the adoption of part two of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not eliminate the effect of the special norm enshrined in Article 57 of the Law of the Russian Federation of December 27, 1991 No. 2124-1 “On the Mass Media,” according to which the editorial board and the journalist are exempt from liability for the dissemination of information that is untrue and discredits honor and the dignity of information if such information is obtained from certain sources (present in mandatory messages; received from news agencies; contained in a response to a request for information; are a verbatim reproduction of official speeches, etc.). In such cases, the editorial office and the journalist are not obliged to check the accuracy of the information, and they cannot be held responsible for the consequences of its dissemination. It is necessary to pay attention to the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated February 24, 2005 No. 3 “On judicial practice in cases of protecting the honor and dignity of citizens, as well as the business reputation of citizens and legal entities.”