Who has the right to recover and for what?
The main feature of contracts in the consumer sphere is disclosed in the Law on PPP - goods, works, services are purchased for personal, household use.
Therefore, the Federal Law is applied in any contracts where one party is a consumer and the other is an entrepreneur:
Free HOTLINE:
Moscow time 8 (499) 938 6124
St. Petersburg 8 (812) 425 6761
Fed 8 (800) 350 8362
- purchase and sale (retail and other);
- household contracting;
- consumer credit;
- rental;
- shipping;
- storage;
- provision of services (any type - water supply, energy supply, etc.);
- other contracts.
IMPORTANT : there are nuances for consumers of services in the financial sector, because... The Federal Law “On the Commissioner for the Rights of Consumers of Financial Services” applies.
The single basis for all cases above is violation of the consumer’s property rights:
- conditions on the quality of goods, works, services;
- obligations to provide information;
- other.
Any buyer, user, or tenant can demand compensation if their rights are violated.
Conditions
The grounds for the emergence of the corresponding consumer right are regulated by Art. 1095 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Individuals and legal entities have the right to make claims for compensation. In this case, the injured party retains the right to choose the person to whom the claim will be addressed: the manufacturer or the seller. Conditions:
- causing property, moral or physical harm resulting from defects in products or services;
- hiding information about defects;
- lack of information about the features of the operation of the product, causing harm to life or health;
- failure to provide comprehensive information about the products specified in the list of Art. 10 ZPP;
- the presence of a cause-and-effect relationship between the actions of the performer, seller, manufacturer in the sale or circulation of goods and the consequences of damage.
Property and moral damage are subject to compensation regardless of the presence or absence of direct intent or fault of the seller, as well as a written agreement on the transfer of the product or the provision of services with the injured party.
The consumer does not have the right to demand compensation if the goods were purchased for the purpose of carrying out business activities.
How to prove the fact of moral harm to the consumer
Since for compensation not only the fact of moral damage is established, but also the guilt of the offender, evidence of the following circumstances is provided:
- the fact of causing suffering;
- the circumstances and specific actions that caused the suffering;
- the causal relationship between the act and the suffering;
- specific suffering (illness, harm to health, etc.);
- amount of compensation.
The Review of Judicial Practice of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 2 of 2020 states that the amount of physical suffering caused by bodily injuries must be proven with a reasonable degree of certainty, because It is not possible to establish it absolutely precisely.
Evidence of moral damage under the consumer protection law is, first of all, documents. The following are used as justifications:
- A certificate from a medical institution about the illness, about undergoing treatment by a psychologist, etc.
- Disease history.
- Expertise:
- forensic psychological;
- forensic psychiatric.
It is possible to invite witnesses to testify.
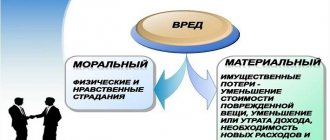
What is called moral damage?
This concept covers suffering of a physical and moral nature caused by poor-quality services or goods. This may include:
- Brief pain.
- Nervous disorder or anxiety.
- Development of mental illness.
- Moral discomfort.
The difference between moral and material harm
Taking into account the legal field under consideration, a violation of consumer rights becomes a prerequisite for the classification of moral damage.
Example A girl went to a hairdresser to get her hair done for a special event. The master made a mistake and burned the client's hair with a hairdryer. As a result, the holiday is ruined, and the girl is depressed because of her appearance. In such a situation, there is poor quality service and moral suffering, which gives the right to compensation for moral damage.
Amount of monetary compensation for violation of rights
Given the specifics of the issue, there are many nuances in determining the amount of compensation.
How to calculate damage
Calculating the harm from suffering is subjective: the citizen himself determines what the cost is.
IMPORTANT: moral damage is neither damage nor loss.
Expenses for treatment, purchase of medicines and others that were required to reduce suffering are not included and are not recovered. All this is material damage or loss.
From this we can conclude that the amount is always different and depends on the situation, the victim, the prevailing judicial practice in the region and even the economic situation of the country.
Minimum and maximum amount
Since the judge is guided by the criteria of reasonableness and fairness, the requirements depend on the evidence provided and other conditions.
The plaintiff has the right to claim any amount of compensation. Judicial practice knows cases when plaintiffs in statements of claim demanded to recover amounts of more than 1 million rubles.
Payment terms
The terms of payment are regulated by the legislation on the enforcement of court decisions. The base period is 2 months from the date of initiation of enforcement proceedings. The defendant can pay the amount before the appointed date.
How to receive compensation for moral damage caused
Considering that the very concept of moral damage is evaluative in nature, it is very important for the plaintiff to act according to the rules in order to prove his case. To do this, you need to follow a certain algorithm that will help you win the lawsuit. Let's consider the main nuances associated with this issue.
Read also: How to get a disability
We prove the fact of causing moral harm
It is quite natural that in order to resolve a conflict situation, you will have to provide evidence that an offense actually occurred.
Words alone will not be enough here. Such issues are usually decided at trial and the court will need compelling reasons to make a decision. The evidentiary procedure is built on three principles:
- The fact of an offense is established. This includes moments when the seller violates the rights of the consumer. For example, the store refused to exchange low-quality products within the time limits established by law. This fact can be proven by a written refusal from the seller or an expert opinion confirming that the product is indeed of poor quality.
- The fact of moral damage is established. Here the plaintiff provides evidence that the situation caused him moral and physical torment. For example, the seller’s actions caused a deterioration in health, provoked stress or the development of a new disease. This fact is confirmed by medical certificates.
- A relationship is established. Here you need to provide evidence that it was the purchase of a low-quality product and the actions of the seller that led to such consequences. This can be confirmed by testimony or other materials.
Addressing the culprits
The next stage will be an attempt to resolve the conflict out of court. To do this, you need to contact the seller or service provider and follow these steps:
- Make a written complaint addressed to the head of the company, detailing the circumstances of the case. Such a document is written in free form; it is advisable to provide links to regulations that protect consumer rights in such a situation.

An example of a claim for poor quality service - Note the desire to resolve the conflict without involving the courts, indicate the amount of monetary compensation for moral damage caused.
- Deliver the claim to the addressee. The claim must be accompanied by copies of documents confirming the applicant’s innocence.
- Wait for a decision to be made. If the manager accepts the complaint for consideration, he has a month to understand the situation. When the company admits its guilt in the incident and agrees to compensate for losses, compensation is paid within 3 days.
Let's go to court
A claim is filed in court in cases where the seller has ignored the claim or the measures taken are not satisfactory to the injured party. The claim is submitted to the court located at the victim’s place of residence. If this is impossible to do for some reason, legal proceedings can be initiated at the legal address of the culprit company or the place of residence of the individual entrepreneur.

Sample statement of claim for moral compensation
Rules for writing a claim
The claim is drawn up in accordance with the form approved by law and displays the following information:
- Full name of the court that will hear the case.
- Information about the plaintiff.
- Information about the defendant.
- A detailed description of the event, in our case, is the purchase of a product of inadequate quality, which resulted in moral harm and the seller’s refusal to resolve the conflict out of court.
- The amount of compensation that the plaintiff plans to receive.
- Evidence presented to the court for consideration.
- List of documents attached to the claim.
Read also: The secret of correspondence
What documents may be required
The claim is supported by all documents capable of confirming the rightness of the plaintiff and certifying the fact of the offense. These include:
- Receipts confirming the fact of purchase of goods from the defendant.
- Testimony of witnesses.
- Expert opinion.
- Medical report.
- A copy of the claim sent to the seller.
State duty amount
Considering that in the situation under consideration we are talking about a violation of consumer rights and compensation for moral damage, there is no need to pay a state fee. In other cases, the legislator sets the duty in the following amounts:
- For individuals - 200 rubles.
- For organizations - 4,000 rubles.
Filing a claim in court
The Consumer Rights Protection Law establishes special places for filing a claim (Article 17):
- at the address where the defendant legal entity is located;
- plaintiff's address;
- place of performance or conclusion of the contract.
Article 15 states that compensation for damage is carried out regardless of other requirements. This means that a claim can only be filed alleging compensation, with no mention of losses, damages or penalties.
IMPORTANT: the claim is filed in the district court.
When to contact
The general period for going to court is established in Article 196 of the Civil Code and is 3 years from the moment the consumer learned of a violation of the right. It is summarized that at the same time the plaintiff experienced suffering.
Required documents
Article 132 of the Code of Civil Procedure establishes the following documents:
- The claim and its copies according to the number of persons participating in the proceedings.
- Evidence supporting the claims in the statement of claim.
In accordance with the POPP (Article 17) and the Tax Code, the consumer is exempt from paying state duty, therefore such a receipt is not attached.
Judicial execution deadlines
The period of execution is regulated by laws on enforcement proceedings. The basic period is 2 months from the date of announcement of the verdict.
Is it possible to appeal court decisions?
Court decisions are appealed in the general manner established by the Civil Procedure Code (Chapters 39, 41, 41.1) by filing a complaint with the courts.
Since the first instance in such cases is always the district court, complaints are filed:
- for an appeal – through a district court of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- for the first cassation – to the presidium of the court of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- for the second cassation - to the judicial collegium of the RF Armed Forces for civil cases;
- for supervision - to the Presidium of the RF Armed Forces.
Regulatory framework
The following documents give the right to compensation for moral damage:
- Law No. 2300-1 - protects the rights of consumers from possible violations by sellers, regulates the procedure for resolving disputes;
- Civil Code art. 151 - defines the principles of moral damage and forms of compensation for damage;
- Civil Code art. 1101 - forms the principles of reasonableness when determining such damage and determines the monetary equivalent of moral suffering;
- Tax Code art. 333.19 - establishes the amount of the state fee when filing a lawsuit.
Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992 No. 2300-1 “On the protection of consumer rights”
Article 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “Compensation for moral damage”
Article 1101 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “Grounds for compensation for moral damage”
Article 333.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Amounts of state duty in cases considered by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, courts of general jurisdiction, and justices of the peace”
Arbitrage practice
Consumers often expect compensation. But the courts do not always satisfy such requirements or approve them partially.
Examples:
- The plaintiff claimed compensation in connection with poor quality services at the trampoline park in the amount of 1 million rubles. The judge refused due to lack of proof of the cause-and-effect relationship (case No. 2-390/2018 of the Moskovsky District Court of St. Petersburg).
- The plaintiff made a claim from the insurance contract in the amount of 100,000 rubles. 5,000 rubles were collected. (case No. 2-1163/2018 in Samara).
- The plaintiff made demands from relations for routine repairs of the property of an apartment building in the amount of 40,000 rubles. 500 rubles collected. (case No. 2-2-2/2018 in Tver).
- The plaintiff claimed from the purchase and sale agreement in the amount of 5,000 rubles. Result of recovery of 1,000 rubles. (case No. 2-1187/2017 in Penza).
How much compensation can I receive?

There is no uniform definition of the amount of compensation for moral damage caused to a consumer in current legislation. There is only a clarification that compensation for non-property damage is permissible in monetary (ruble) equivalent. The amount of compensation is determined by the injured party independently. But the stated amount of compensation is not necessarily paid in full. There are two options for settling the amount of payments:
- by agreement between the consumer and the manufacturer;
- at the discretion of the court.
The parties to the relationship are free to establish a specific amount of compensation that satisfies both the victim and the perpetrator. If it was not possible to agree on a single amount of payments, then a forced recovery is ordered by the court if the circumstances of the case are proven and the requested money is justified. Judges are guided by the fact that the amount of moral damage in cases of violation of consumer rights must correspond to the standards of reasonableness and objectivity. The demand to recover several million rubles for the sale of a kilogram of rotten vegetables will not be satisfied in full in court.
In practice, moral harm to the consumer is assessed based on the degree of guilt of the manufacturer (seller), the amount of damage incurred, the degree of harm to the consumer and additional circumstances (Article 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The court takes into account the financial situation of the plaintiff and defendant, the location (residence) of the parties, and regional characteristics. However, the degree of compensation for property damage does not affect the determination of the amount of compensation. Damage caused to a person is fully compensated (Article 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Return of defective goods to the seller and compensation for losses
By virtue of paragraph 2 of Article 15 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, losses are understood as real damage and lost profits. Real damage is the expenses that a person whose right has been violated has made or will have to make to restore the violated right, loss or damage to his property. Lost profits are lost income that such a person would have received under normal conditions of civil transactions if his right had not been violated. - demand the replacement of goods of inadequate quality with goods that comply with the contract. An exception is the case when the seller, having received notification from the buyer about the shortcomings of the goods supplied, immediately replaced them with goods of proper quality. A clear non-compliance of the goods with the quality established by the technical specifications is a significant violation of the requirements for the quality of the goods. In accordance with paragraphs 1, 2 of Article 393 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the debtor is obliged to compensate the creditor for losses caused by non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of the obligation.
24 Dec 2020 marketur 175
Share this post
- Related Posts
- How to write an entry in a work book that is invalid
- Child Benefit for Single Mothers in 2020 in the Sverdlovsk Region
- How to properly terminate a contract with a monopoly
- Benefits for kindergarten 2020 Bryansk for large families
How Article 15 interacts with other legal norms
For example, Article 18, which regulates the rights of consumers when defects are discovered in goods.
Both orders do not contradict each other in meaning and direction. After all, if a buyer identifies illiquid assets from a supplier who is obliged to provide only fresh and high-quality products, he has the right to demand:
- replace the product;
- reduce cost;
- return money;
- eliminate identified defects in the product.
This is in accordance with Article 18; the buyer can also take advantage of Article 15 and demand the seller compensate for the moral damage caused to him.

Laws and circulars developed in the Russian Federation try to take into account all possible cases so that the rights of citizens are always protected. Therefore, from time to time there is a revision and revision of existing acts. From there, amendments and additions to legislation arise.