Features of the crime
Moderate injuries include all injuries that:
- cannot lead to human death;
- did not cause loss of hearing, vision or functionality of any organ of the human body;
- did not lead to termination of pregnancy;
- did not cause a mental disorder;
- are not expressed in irreparable disfigurement of appearance;
- did not induce permanent disability or the inability to engage in a certain type of activity.
At the same time, causing such damage leads to long-term loss of health and loss of ability to work for a period of more than 3 weeks. Examples of such injuries include joint dislocations, small bone fractures, soft tissue injuries, etc.
The subject of the crime may be a person over fourteen years of age who intentionally or unintentionally committed actions that resulted in injury to the victim.
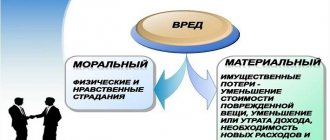
The difference between moral hazard and harm to health
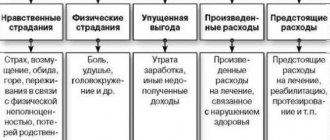
Moral damage is interrelated physical and moral suffering:
- after surviving an attack;
- influence or inaction;
- entailing irreparable or difficult to repair damage to the health and life of the victim;
- this or that encroachment on property and legal interests.
Harm to health is the infliction of bodily injury to one degree or another, which leads to various diseases or loss of organs.
Such damage requires physical compensation in the form of:
- treatment;
- operations;
- therapy.
They always occur when the culprit intentionally or carelessly influenced the anatomical integrity of the victim’s body. And they always pose a danger not only to the health, but sometimes even to the very life of the injured party.
Just like moral, physical injury must be immediately compensated by the culprit.
The difference between these concepts is that the victim undergoes moral suffering in the event of moral harm:
- insults;
- a person’s feelings or ideological principles are hurt;
- his moral, ethical and other rights are affected.
And in case of damage to health, it bears physical consequences:
- beatings;
- deprivation of organs or their functions;
- poor health;
- chronic or acute conditions of organs, etc.).
Due to these differences, the calculation process and the amount of compensation for damage caused also differ. Thus, in case of moral damage, the amount of payment is determined by the victim or the court, taking into account the claim of the injured party and all the circumstances of the dispute.
And in the event of harm to health, first of all, the costs of treatment and restoration of health must be covered.
Liability for intentional causing of harm
According to Art. 112 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, intentional infliction of harm of moderate severity entails punishment for the perpetrator in the form of:
- imprisonment or restriction of freedom for up to 3 years;
- forced labor for a period of up to 3 years;
- arrest for a period of up to six months.

At the same time, the presence of aggravating circumstances leads to the fact that the sentence may be imprisonment for a period of up to 5 years. Aggravating circumstances include:
- Causing injury to two or more persons.
- Causing harm to a person or his relatives, when the cause of the crime was official activity or the performance of public duty by the victim.
- Committing actions against a minor or a person who was in a helpless state at the time of the crime.
- Commitment of an act by a group of persons, including by prior agreement.
- Committing a crime with hooligan intent, for political, ideological reasons, as well as on the basis of racial, ideological, religious or national enmity (you can find out about criminal liability for hooliganism here).
- Use of weapons or other objects that can be used instead of weapons to cause injuries.
It is worth noting: if the victim intends to initiate a criminal case based on the fact that he received bodily injuries, he must file a statement of battery with law enforcement agencies.
Law enforcement officers will send the victim for a forensic medical examination, which will determine the severity of the damage to health. In accordance with this, the appropriate article of the Criminal Code will be selected to qualify the crime and a criminal case will be initiated. A crime is considered committed intentionally if it is proven that at the time of inflicting moderate injuries the perpetrator was aware of the consequences of his actions and could not have committed them. However, he was in a normal mental state.
Criminal liability arises only if the injuries are severe (Article 118 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Criminal liability under Article 112 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is discussed in the following video
Damage compensation procedure
It all depends on whether the person at fault for the accident has a compulsory motor liability insurance policy or not.
If insurance is available, the victim can apply for payment from the offender's insurer. He needs to provide documents confirming moderate harm to health in an accident.
The insurer reviews the papers within 20 days, after which it makes a decision on paying the insurance compensation or refusing to transfer funds. For missed deadlines, a penalty will be charged.
The maximum amount of compensation for damage to health under compulsory motor liability insurance is 500 thousand rubles.
If the culprit does not have a compulsory motor liability insurance policy, or he himself is unknown, you can apply for compensation to the Russian Union of Auto Insurers.
If the amount received was not enough to restore your health, or you were refused payment, the money must be demanded from the person responsible for the accident.
Causing harm in a state of passion or by exceeding necessary self-defense measures
Additionally
In the event that death due to negligence occurs from harm caused in a state of passion, this crime is qualified under Art. 113 and 109 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (Causing death by negligence). Moreover, when assigning a punishment, the court must take into account Part 3 of Article 61, which prohibits the use of mitigating circumstances twice. That is, the state of passion already acts as a qualifying sign of a crime, therefore it is impossible to mitigate the punishment in connection with “the unlawful or immoral behavior of the victim, which served as the reason for committing the crime” (clause “h” of Part 1 of Article 61).
Often in judicial practice there are cases where the perpetrator caused harm to the victim in a state of passion. This condition means strong psychological disturbance, which was caused by violence, bullying or insults on the part of the victim, or the creation by the victim of a long-term psychologically traumatic environment for the perpetrator.
If it has been proven in court that moderate or severe damage was inflicted in a state of passion, then the perpetrator, in accordance with Article 113 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, may be sentenced to one of the following punishments:
- correctional or forced labor for a period of up to 2 years;
- imprisonment or restriction of freedom for a period of no more than 2 years.
According to Article 114 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, infliction of moderate bodily harm that occurred as a result of exceeding permissible self-defense is punishable in the same way, but for a period of no more than one year.
If the damage was caused as a result of exceeding the measures that were necessary to detain the offender, then the maximum period is two years.
Also, in cases of bodily injury, the victim has the right to file a claim in court for compensation for material costs associated with treatment and rehabilitation, as well as for moral compensation. About compensation for damage caused by a crime in criminal proceedings, read the article https://lexconsult.online/6114-protsedura-vozmeshheniya-vreda-prichinennogo-zhizni-ili-zdorovyu-grazhdanina.
Watch this video about intentionally causing moderate harm to health.
How to obtain compensation for personal injury from the person at fault in an accident?

You should contact the person responsible for the accident after receiving a medical report.
First, write him a claim demanding compensation for moderate damage to health. In the document, indicate the amount, terms and desired procedure for compensation.
The claim can be submitted in person or sent by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery.
If he ignored your request or refused, you should apply to the court for compensation for damage received as a result of the accident.
Submitting a claim to the person at fault for the accident is an optional procedure. You can immediately go to court.
How to file a claim?
The statement of claim is written according to the rules established by Art. 131 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. It should contain:
- name and address of the court that will hear the case;
- information about the plaintiff and defendant (full name, addresses, telephone numbers);
- a detailed statement of the circumstances of the case;
- the reasons why you are claiming damages;
- the amount you wish to recover from the defendant;
- information about pre-trial settlement of the dispute.
Please attach to your application:
- certificate of accident;
- calculation of the required amount;
- an extract from an outpatient card, checks and receipts confirming the amount of costs for restoring health;
- a medical examiner's report on the severity of your injuries;
- a certificate from your place of work about your average earnings.
All requirements must be documented.
The papers are transferred to the judicial authority at the defendant’s place of residence. If the cost of the claim does not exceed 50 thousand rubles, the case will be considered by a magistrate. If the amount of the claims presented is greater, the case is transferred to the district (city) court.
An example from judicial practice
Citizen Ivanov, in front of witnesses, initiated a fight with gr. Petrov, as a result of which he received injuries: bruises, broken fingers and a 1st degree concussion. Petrov was in outpatient treatment for 30 days. During the investigation, it was found that the cause of the fight was systematic insults to the citizen. Petrov Ivanov, including insults were committed immediately before the moment of the fight. The expert provided an opinion that at the time of the crime Ivanov was in a state of passion. He was sentenced by the court to correctional labor for a period of 1 year.
Our specialist will answer all your questions on the topic of the article in the comments.
Causing damage to health
This can be not only the negligence of doctors, the negligence of nurses or some other personnel of a hospital, clinic or clinic, but also the infliction of harm by other persons.
For example, by hooligans, relatives, friends at a party, law enforcement agencies, and even a court decision, which can cause a number of diseases or exacerbations due to nervousness.
Unlawful judicial act
If a judge has made a deliberately unauthorized, or rather unjust, sentence, act or decision, then this is considered a crime and such a judge or judges may be fined. Such situations are regulated by Art. 305 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Find out how to draw up a claim for compensation for moral damage from the article: statement of claim for compensation for moral damage. Read information on determining the amount of compensation for moral damage here.
A fine is levied on the culprit in the amount of up to 300,000 rubles. or in the amount of the minimum wage established by law in a particular region of the country, or the income of the convicted person for a period of up to 2 years.
In addition to fines, the offender may also be punished with imprisonment for up to 4 years.
And if his illegally justified sentence entailed serious consequences for the convicted person in the form of imprisonment, then the judge could be sent to prison for up to 10 years, depending on the severity of the crime.
Behind the open hatch
Compensation for damage to property or health due to an open hatch is regulated by Art. 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and is made through a court decision. This law obliges the culprit to compensate the victim in full for the damage, including such organizations as housing and communal services and others.
These organizations are responsible for closed sewer manholes. Also, the company responsible for safety and closed hatches is responsible before the law - Art. 1068 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which states that a legal entity may be liable for the negligence of its employee.
Caused by a source of increased danger
If harm to health was caused at work by any source of increased danger, then the enterprise, as a legal entity, is obliged to compensate for this damage. This liability is regulated by Art. 1079 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which states that it is legal entities or civilians who compensate for damage.
This damage can be caused by:
- dangerous reagents;
- poisons;
- chemicals;
- explosive substances;
- mechanisms powered by electricity;
- radioactive substances and others.
The commission must also find that the victim did not have his own personal intent when inflicting injuries on himself, and that there were no force majeure circumstances that led to the incident.
When bitten by a dog
Material damage is compensated according to the legislation of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in accordance with Article 1064. All compensation for mental suffering due to dog bites is regulated by Art. 151 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation with accompanying monetary compensation for wound treatment.
If the case is resolved through the court, then the amount of compensation is determined by the judicial authority, depending on the degree of guilt of the owner of the dog, as well as certain circumstances that deserve attention. After all, it may happen that someone provoked the dog to attack.
However, the opposite may also be true - the dog and its owner were walking without a leash or muzzle. In this case, the owner must be held accountable before the law for the attack of his pet.
In case of an accident
During an incident in the form of an accident, in addition to the culprit, the victims are reimbursed benefits from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation (Articles 220-227 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, the benefit is paid:
- for temporary disability;
- insurance;
- medical treatment costs are covered;
- expenses for social or professional rehabilitation procedures.
Broken arm
Compensation for this damage to health in the performance of any obligations, including contractual ones, is regulated by Article 1084 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Also, the amount of lost earnings that the causer of damage must compensate to the victim in the event of damage to his health, including a broken arm, is coordinated using this article.
In addition, in the case of a deliberate private attack on the victim, sentences to punish the culprit are made on the basis of Art. 162 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Compensation for harm of moderate severity or for moderate harm to health due to a broken arm by the culprit is carried out in full on the basis of a court decision.
When the silence is broken
If your home is often or regularly disturbed by silence at night, then you may well sue the violators. An administrative offense for Moscow and the Moscow region is regulated by the law “On ensuring peace and quiet of citizens in the Moscow region” No. 16/2014-OZ.
The law was signed by the governor on March 7, 2-014, and officially published on the portal of the Government of the capital on March 12, 2020. Legal norms regulate the time of peace and quiet for citizens from 21:00 to 8:00 on weekdays and from 22:00 to 10:00 on weekend days of the week.
Table. Amounts of fines for violating silence (For Moscow and the Moscow region)
| Type of fine | Who pays | Amount of fine |
| when ignoring a warning in case of disturbance of silence | for individuals | 1000-3000 rub. |
| for officials | 5000-10000 rub. | |
| for legal entities | 20000-50000 rub. | |
| For repeated violation of silence | for individuals | 4000 rub. |
| for officials | 15000-30000 rub. | |
| for legal entities | 60000-80000 rub. | |
| the third time and subsequent regular violations of silence are punishable by a fine | for individuals | 5000 rub. |
| for officials | 50,000 rub. | |
| for legal entities | 100,000-150,000 rub. |
Violation of silence is considered:
- loud sound from TV and other home equipment;
- sound amplification devices operating during prohibited hours;
- street hooligans shouting, whistling, singing and playing loud musical instruments;
- inaction of car owners whose alarms went off at night;
- use of pyrotechnics at night;
- repairs, construction, loading operations during silence.
Police officers and law enforcement officers have the authority to impose penalties for violating silence, so victims simply need to write a statement at the nearest police station.
Punishment for causing moderate harm to health: features
The crime we are considering is the subject of several articles in criminal law. Separate norms include causing moderate harm to health in a state of passion (Article 113 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation) or due to unacceptable self-defense (Article 114 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
Here the punishment is more lenient than for an intentional crime. For example, the maximum penalty for medium bodily injury while in a state of passion is 2 years in prison.
If the victim’s health was damaged due to excessive self-defense, then the most severe punishment for the perpetrator is 1 year in prison.
Taking into account other mitigating circumstances, the offender’s imprisonment may be replaced by correctional labor. In any case, the future fate of the person will be decided by the court, based on all the materials of the case.