Submitting a claim to the employer for non-payment of wages is a legal way to resolve the problem out of court. And the organization is no less interested in this than the employee. If such cases go to court, the overwhelming majority are decided in favor of the employee. And then, in addition to the forced recovery of earnings, the company will face penalties, compensation for moral damages to the plaintiff, reimbursement of legal expenses and other additional damages.
Salary payment procedure
The employer is required to pay labor costs 2 times a month. Specific dates for payments must be indicated in the employment agreement or in the documentation reflecting the procedure for issuing money. Today there is no talk of an advance. Amounts that are issued no later than 15 days (calendar) from the end of the period for which they were accrued (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are actually earned. They cannot be either 20% or 40%, as is often the case in practice - only payment for time worked. Deviation from these standards is a violation of labor laws.
When funds are not received on time, the employee is entitled to compensation payments. Their size is calculated based on 1/150 of the Central Bank key rate for each missed day for the entire overdue amount (Article 236 of the Labor Code, Article 2, 4 of Law No. 272-FZ of 07/03/2016). From June 19, 2017, the rate is 9% (Central Bank Decree No. 3894-U dated December 11, 2015). Some organizations have standards that differ from those specified in the law. They can be more, but never less.
The 1st day of delay is considered to be the date following the one set for payment of wages. The last one is the date when the money was paid. The basis for calculating interest is the accrual minus income tax. Compensation is due regardless of the fault of management.
In order to combat such violations, there are several ways. One of them is a claim for non-payment of wages written to the management.
Guarantees of labor legislation
The work of every working person must be paid. If the director delays wages, this is a violation of the Labor Code. In accordance with Article 21 of the Labor Code, a working citizen must receive earned money in full and on time, the amount of which is specified in the contract in agreement with the company management.
If wages are not paid within 15 days, employees have the right to suspend work. Until a written commitment is provided by the director to promise to pay wages on a certain date, employees may not come to work. In this case, days must be paid at the average wage.
After receiving the notification, citizens are required to begin performing their official duties the next day. If employees do not report to work after notification, this is considered absenteeism and may lead to dismissal.
Please note! Article 236 of the Labor Code establishes the obligation of the manager to return the delayed wages along with compensation. In addition, on the basis of Article 237, the employee has the right to recover through the court moral damages for the delay of funds.
How to make a calculation
It is advisable to consider an example of compensation calculation, which should be attached to the pre-trial claim or placed in its text.
Salary at LLC "White Sail" is issued:
- 25th of the current month;
- 10th day - the day following the day on which the salary was accrued.
Designer Kuznetsov V.A. works 5 days a week. He received his salary for June 2017 on August 31. June earnings amounted (minus income tax) to 80,000 rubles. For the 1st and 2nd half of June, 40,000 rubles are payable.
June 25 is a non-working day, the day of payment of the first 40,000 rubles. – June 23. Delay from June 24, 2020 to August 31, 2020 – 69 days.
40,000 x 9% x 1/150 x 69 days. = 1656 rub.
Day of payment of the second 40,000 rubles. – July 10, 2020. Delay from June 11, 2020 to August 31, 2020 – 52 days.
40000.00 rub. x 9% x 1/150 x 52 days. = 1248 rub.
The total amount of compensation to Kuznetsov V.A. will be 1656 + 1248 = 2904 rubles.
When the employer does not agree to satisfy the demands of a subordinate, expressed orally, you need to contact him, setting out the claims on paper.
Take note! Before drafting a document, it is worth talking with colleagues. They may also have suffered from non-payment and are ready to defend their rights. Then a collective claim is drawn up, which can be more effective.
How to write an application for suspension of work
In accordance with labor legislation, employees have the right to suspend the work process if the director of the enterprise does not pay wages for more than 15 days. They may not go to work until the full amount of the debt is received. Penalties must also be paid for all days of delay.
If one of the employees in the team decides to stop working, he notifies the employer in writing. A warning may be filed with the complaint or after it is filed if the director does not respond to the demands.
Please note! According to labor legislation, in the event of a suspension of work due to lack of wages, a person may not come to the enterprise at all. But for all these days he should be paid a salary in accordance with the average amount. But as soon as the management of the organization notified employees about the timing of the issuance of money, the next day the person starts work.
Not all cases allow you to pause a workflow.
This is prohibited if:
- a person works in a hazardous industry;
- a state of emergency has been declared in the city;
- The employee’s work is related to ensuring the livelihoods of the population.
The labor process of military personnel, civil servants, and employees of the Ministry of Emergency Situations cannot be suspended.
Form and content
A complaint to an employer about non-payment of wages is written in any form, but there are a number of points that it is advisable to reflect.
This:
Part 1 – introductory:
- Company name.
- Full name of the general director (other first person) indicating the position held.
- Employee's full name.
- Position or profession.
- Structural unit (if any).
- Name of the document (Claim, Application).
Part 2 – main:
- Subject of disagreement: delay of PO.
- An indication of the duration and amount of the debt incurred.
- Designation of provisions of labor legislation indicating violations.
- Link to the employment agreement with information:
- about his number
- about the date of signing,
- about the amount of salary or tariff rate,
- about the work schedule,
- about the days of payment of wages.
- Date of last receipt of money.
- Last amount received.
- Calculation of compensation payments.
- An indication of previous appeals - oral and written (if any).
Part 3 – final:
- Proposals for a way out of the situation: payment of wages and compensation (according to calculations) indicating specific deadlines.
- A warning about measures that will be taken if the requirements are not met on time and in full. They will be discussed below.
- Links to laws that provide for employer liability for late salary payments.
- Date, signature.
Structure of a claim against an employer
There is no fixed form for writing an appeal to an employer with a demand to repay a salary debt. However, when drawing up a claim, it is better to adhere to certain standards adopted for business papers. A document requesting payment of wages must contain the following elements:
- Introductory part, which indicates: Name of the enterprise;
- Name of the position and full name of the manager to whom it is addressed;
- Position and full name of the person applying.
- Period of employment with the employer and position held;
- Pay off existing salary arrears;
The right to compensation for moral suffering is enshrined in Art. 237 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The claim is submitted in person or sent by registered mail with notification. There are no specific deadlines for responding to such letters by law, but in practice they do not exceed 2 weeks.
Adviсe
Here are some tips on how to write a complaint to an employer and present it correctly.
The claim can be presented personally to the boss, the secretary, or sent by mail. In the first 2 cases, a mark of receipt with a signature, its transcript, indication of the position held and the date of receipt is required on the second copy. In the latter, the letter must be registered and with notification. Typically, this method is used when management refuses to personally receive papers.
In Part 2, special attention should be paid to information about events (if any) that resulted in such negative consequences as:
Late payments:
- for a loan - with the accrual of penalties and the bank filing a statement of claim in court or transferring debts to collectors who resorted to threats;
- for utilities - with a power outage, water supply;
- for educating children at a university - with their expulsion.
Exacerbation of the disease due to the impossibility of treatment in a paid clinic or the purchase of expensive medications.
Mention of such consequences can awaken a sense of responsibility in the manager, who has not only left the subordinate without the opportunity to satisfy urgent needs, but also caused him significant damage. It can be both material and moral and is collected through the court.
It is important to indicate in the 3rd part the specific deadline for fulfilling the claims. It can be indicated either in the form of a specific date or in the number of days given to resolve the issue. It is imperative to clarify which days these are – working days or calendar days.
Claim for collection of arrears of wages
LLC "__________________" Legal address: __________________ Actual address: __________________
From ___________________________ Address: _____________________________
____________, I, ______________, was actually hired in the marketing and advertising department of LLC "_____________" (legal address: _________________________) for the position of brand manager, but the employment contract was concluded with me only on ________. (Order No.______ dated ____________). Throughout my entire career, I conscientiously fulfilled my job duties, did not violate labor discipline, did not have any penalties, and valued my reputation. The employer LLC "___________" gave me wages in two ways: one part of the wages in the amount of __________ rubles according to pay slips, and the other part of the wages in the amount of ___________ rubles in cash "in an envelope", which are not taken into account when taxing this organization. ___________ g. The employment contract concluded between me and LLC “______________” was terminated on my initiative in accordance with clause 3, part 1, art. 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Order No._____ dated ____________). Upon dismissal, I was given my work book and paid part of my salary in the amount of _______ rubles. However, part of the salary in the amount of ________ rubles for the last 2 months (the total amount of debt is ________ rubles) was not paid to me. The employer did not explain any reasons or grounds for this non-payment. In accordance with Art. 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, upon termination of an employment contract, payment of all amounts due to the employee from the employer is made on the day of the employee’s dismissal. If the employee did not work on the day of dismissal, then the corresponding amounts must be paid no later than the next day after the dismissed employee submits a request for payment. In the event of a dispute about the amount of amounts due to the employee upon dismissal, the employer is obliged to pay the amount not disputed by him within the period specified in this article. Thus, all amounts due to the employee from the employer were not paid to me on the day of dismissal. These actions of the employer put me in a difficult financial situation and created negative consequences for me, since I was forced to borrow money from friends and acquaintances and resort to using a credit card several times.
In accordance with Art. 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, based on generally accepted principles and norms of international law and in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the basic principles of legal regulation of labor relations and other directly related relations, among others, recognize the right of every employee to timely and full payment of fair wages ensuring a decent human existence for himself and his family, and not lower than the minimum wage established by federal law. According to Art. 1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the goals of labor legislation are to establish state guarantees of labor rights and freedoms of citizens, create favorable working conditions, protect the rights and interests of workers and employers. In accordance with Art. 355 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the activities of the federal labor inspectorate and its officials are carried out on the basis of the principles of respect, observance and protection of human and civil rights and freedoms, legality, objectivity, independence and transparency. The main tasks of the federal labor inspectorate are: ensuring compliance and protection of labor rights and freedoms of citizens, including the right to safe working conditions; ensuring compliance by employers with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards; providing employers and employees with information on the most effective means and methods of compliance with the provisions of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms; Article 360 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the procedure for organizing and conducting inspections of employers. The subject of the inspection is the employer’s compliance in the course of its activities with the requirements of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, compliance with orders to eliminate violations identified during inspections and to take measures to prevent violations of labor law norms and to protect the labor rights of citizens. One of the grounds for conducting an unscheduled inspection is an employee’s request or statement about the employer’s violation of his labor rights. Thus, I was forced to file a complaint with the Department of State Tax Inspectorate of the Moscow Region for the Central Territorial District of Supervision to protect my violated rights. In accordance with Art. 362 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, managers and other officials of organizations, as well as employers - individuals guilty of violating labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, are liable in cases and in the manner established by the Labor Code and other federal laws. To resolve this labor dispute and draw up a statement of claim and claim addressed to you, I had to seek legal assistance from LLC “___________”, paying money in the amount of ___________ rubles for the service provided to me. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 15 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a person whose right has been violated may demand full compensation for the losses caused to him, unless the law or contract provides for compensation for losses in a smaller amount. Clause 2 of Art. 15 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that losses are understood as expenses that a person whose right has been violated has made or will have to make to restore the violated right, loss or damage to his property (real damage), as well as lost income that this person would have received in normal circumstances. conditions of civil circulation, if his right had not been violated (lost profits). Since I do not have a legal education, and drawing up a claim is difficult for me, I do not have knowledge of the rules of civil procedure, I needed to seek legal assistance, and in this regard, I believe that I have the right to compensation for the expenses I incurred for legal services in full. In accordance with Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, moral damage caused to an employee by unlawful actions or inaction of the employer is compensated to the employee in cash in amounts determined by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. In the event of a dispute, the fact of causing moral damage to the employee and the amount of compensation for it are determined by the court, regardless of the property damage subject to compensation. I estimate the moral damage caused to me by the illegal actions of my employer at ________ rubles.
What are employers warned about?
As already mentioned, in the complaint it is advisable to indicate the measures that will be taken if the management does not respond to the demands set out in it.
Such measures are:
- Suspension of activities.
- Contacting the labor commission.
- To the judges.
- To the prosecutor.
Absenteeism
When the salary is delayed by more than 15 days, the person may not work until the day he receives the money. This is stated in Art. 142 TK. He must notify the manager in writing, also certifying in writing the receipt of the document. The same rules apply here as when filing a claim. And also a warning is sent by mail in case of refusal to sign the 2nd copy.
Suspension of activities is carried out from the date when the application for this was received. During downtime for the reason in question, average earnings are paid. (Article 142 of the Labor Code, Law No. 434-FZ, Review of the Supreme Court of March 10, 2010). You must resume your duties no later than the day (working day) that follows the day you receive a notification from your superiors that they will pay the debt on the day you leave.

Not all employees can interrupt their work duties. The following are not entitled to do this: military personnel, civil servants, persons involved in particularly hazardous industries, performing functions of ensuring energy, heat and water supply, communications, emergency medical care (Definition of the Const. Court No. 60-O dated 03/02/2006). Work cannot be stopped during either a martial law or a state of emergency.
Complaint to the labor inspectorate
The main thing to consider when sending papers to this authority:
- The application is accompanied by a copy of the employment agreement and evidence of late payments (if any).
- In addition to submitting an application in person or sending it by mail, you can use the Internet.
- The period for studying a complaint is 30 days from the date of receipt (there are cases of extension up to 30 days).
- If a person wants the employer not to know about the source of information, this circumstance must be indicated. In this case, maintaining incognito is the responsibility of the inspectors (Article 358 of the Labor Code).
- After the inspection, in addition to payment orders, inspection staff will monitor their implementation. The issue of applying sanctions to the employer is also being considered.
Judicial option
Questions about non-payment of salary can be addressed within 1 year from the date on which it should have been received. An application for a court order must be sent to the magistrate located at:
- work;
- your residence;
- finding an employer.
A court order plays the role of a writ of execution. It is issued within 5 days from the date of application. No one is summoned to court. A copy of the order is sent to the employer. If he has objections, he can submit them within 10 days. Then the order is canceled, and the dispute must be continued within the framework of the claim proceedings.
When there are no objections, the judge issues a 2nd copy. an order with an official seal for presentation to management for the purpose of execution. If you wish, you can write a statement requesting the transfer of the document to the bailiffs. According to Art. 211 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, an order to pay wages for 3 months is subject to immediate execution. You can also demand compensation for moral damage through the court (Article 237 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There is no need to pay state fees or court costs.
Important! If the amount of the claim is more than 500 thousand rubles, you need to go to court with a claim.
The application to the prosecutor's office is written in accordance with the provisions of Law No. 2202-1-FZ dated January 17, 1992.
What threatens the employer
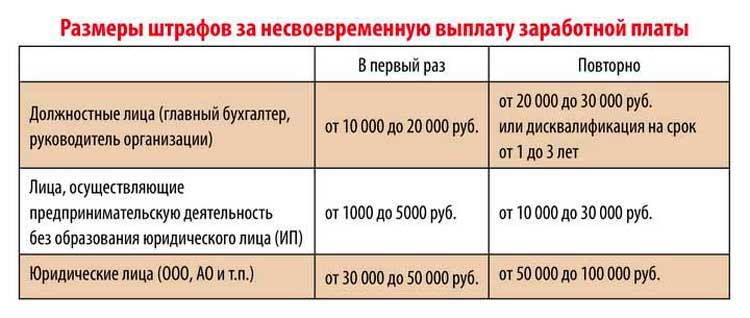
As stated in Art. 5.27 of the Administrative Code, when there is an unpaid salary or its incomplete payment on time, this is followed by a warning, fine, and disqualification.
| Category | Penalties (thousand rubles) | |
| First violation | Repeated | |
| Executive | 10-20 | 20-30 or disqualification for 1-3 years |
| IP | 1-5 | 10-30 |
| Entity | 20-30 | 50-100 |
According to the Criminal Law (Article 145.1), if the ZP is delayed, the following penalties are faced:
| Sanction | Features of non-payments | ||
| Partial, more than 3 months, for selfish reasons motives | More than 2 months. full or in an amount less than the minimum wage, out of selfishness motives | If serious consequences occur | |
| 1. Fine | Options:
| Options:
| Options:
|
| 2. Deprivation of the opportunity to occupy a certain position. due | up to 1 year | In addition to clause 3 | In addition to clause 4 |
| 3. Force. work | up to 2 liters | up to 3 liters + clause 2 – up to 3 years or without it | Not provided |
| 4. Imprisonment | up to 1 year | up to 3 liters + item 2 – up to 3 liters / without | for 2-5 l. + item 2 – up to 5 years / without |
Attention! A partial payment means an amount that is less than half of your earnings.
To write a claim for non-payment of wages and achieve elimination of violation of labor rights, you need to familiarize yourself with a lot of information. But equally important is a determined attitude. Therefore, the document cannot be drawn up by limiting itself to a formal approach. It is necessary to convey to the unscrupulous employer the idea that he is right and the punishment that threatens him. You can report a delay in your salary to the hotline of the Public Chamber of the Russian Federation by phone: 8-800-700-8800.
Features of the complaint to the employer
If you decide to write a claim to your employer, then, depending on the reason for filing such a document, check the statute of limitations for the labor dispute. So, in cases of reinstatement to work, they are only a month.
In such cases, it is better to file a claim, as well as a complaint to the labor inspectorate and the prosecutor's office of the Russian Federation. It's much more efficient.
In addition, in the vast majority of cases, working for an employer is extremely uncomfortable. Therefore, people are reinstated, collect wages and quit of their own free will.
A pre-trial claim to an employer is drawn up according to general rules. In the text of the document you indicate the essence of the dispute, provide arguments for the illegality of the actions of the employer or its representatives in the organization and your requirements.
The employer has the right to verify the information specified in the complaint and bring the perpetrators to disciplinary action. Therefore, in such cases, the results of the claim will have to wait.
Employer's liability for non-payment of wages
An employer who fails to pay its employees on time may be held liable. There are three main types of liability for such illegal acts: criminal, administrative and material.
Usually, employers are brought to criminal liability if they are late in receiving wages on a particularly large scale, or if it affects a wide range of employees.
Administrative liability provides for punishment in the form of fines or suspension of the organization’s work. It occurs for the employer, according to Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences. The amount of the fine depends on whether the offense was committed for the first time or a second time and the category of the offender: legal entity, entrepreneur or official:
- In case of primary violation of the law, the entrepreneur faces a fine of 1000-5000 rubles. , for secondary – 10,000-30,000 rubles.
- For organizations, a larger amount of penalties is provided - 30,000-50,000 rubles. for the first violation and 50,000-100,000 rubles. for legal entities.
- For officials, the amount of liability is 10,000-20,000 rubles. , for repeated violations - 20,000-30,000 rubles.
The employer's financial liability implies that the employer accrues and pays compensation to the employee for each day of delay in payments. Compensation is paid from the next day of salary delay.
In general, compensation is paid in the amount of 1/50 of the refinancing rate of the debt amount for each day of delay. But the collective agreement may provide for greater employer liability.
Thus, a claim for non-payment of wages by the employer is drawn up in a free format and in writing. It consists of an introductory part with information about the employer and employee, motivational and operative parts of the document. It indicates the employee’s demands for repayment of debt to him and payment of a penalty for late obligations. The claim should refer to the provisions of the Labor Code and the terms of the collective or labor agreement.
Dear readers, each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call :
Or on the website. It's fast and free!
Contents of a claim for non-payment of wages
References to the above articles of the Labor Code are usually present in the application drawn up by the employee. Before writing a complaint to your employer, it is useful to look at the Criminal Code. This will allow the negligent management to be reminded of the contents of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code. In accordance with this rule, for deliberate failure to pay wages for more than 2 months, you can be imprisoned for 3 years. If the lack of money in the family (due to the fault of the employer) has led to serious consequences, the responsible person can be jailed for up to five years. For example, if non-payment of wages to the father of the family led to the fact that the parents had nothing to buy medicine for the child, which is why his condition sharply worsened.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
Moscow and region St. Petersburg and region All regions of the Russian Federation It's fast and free!
A letter of claim is sent to the head of the company that failed to pay the employee’s wages in a timely manner. The main purpose of this document is to warn superiors about the employee’s intention to fight for his rights. A claim for violation of deadlines for payment of wages is the last opportunity to peacefully resolve the labor dispute that has arisen.
The complaint informs the organization's management about the violation of the employee's labor rights and tells what exactly it is. In this case, the employee must indicate:
- from what time and in what position has he been working in the company, on the basis of what employment contract;
- what amount of salary is guaranteed to him by the signed contract;
- how long has he not received the funds he earned;
- what is the amount of debt generated?

The following lists what legal norms are violated by such actions of the employer, and what he faces for this. Then, as a rule, there follows a demand for compensation for moral damage (indicating the exact amount), and justification for what exactly it was expressed in:
- worries due to the fact that the family has been short on money for a long period of time;
- inability to buy necessary medications;
- poor child's diet;
- the need to postpone a long-planned trip or visit to the doctor:
- disrespectful attitude towards an honest employee, ignoring his legal requirements, etc.
Here, if necessary, the employee reports how much he spent on legal services. In the final part of the document he suggests:
- pay him all salary arrears;
- compensate for moral damage;
- reimburse the costs of legal assistance.
The pre-trial claim ends with a warning that if the listed requirements are ignored, the employee will continue to defend his rights and interests in the judicial and regulatory authorities. Similar statement:
- or it is handed over to the employer personally (in which case it is necessary to make a mark on the second copy;
- or sent to him by mail (then you should issue a registered letter, describing its attachment).
The law does not specify the exact period within which the company’s management is obliged to respond to the application received. However, according to established practice, 10-14 days are considered a reasonable time for response.
Is there any point in filing a complaint?
The claim can hardly be considered an effective way to solve problems arising in the relationship between the employee and the employer. The fact is that the employer’s actions are rarely spontaneous.
This means that the employer justifies and considers any of his actions in one way or another, thus a claim that does not oblige him not only to satisfy the requirements contained in it, but even to simply respond to it, is unlikely to bring at least some result.
However, writing a claim may be justified, for example, in cases where:
- the dispute is not fundamental for the employer, and he can satisfy the employee’s demands so as not to provoke the initiation of civil proceedings;
- the writing of the claim is caused by the need to suspend the statute of limitations. This can happen if for some reason the statute of limitations is coming to an end and the employee does not have time to file a claim in court;
- writing a claim is caused by the need to create an additional evidence base for the court, for example, in the case where the employee does not have confirmation of the existence of an employment relationship with the employer.








