What is working at height?
Work at height includes actions that an employee performs at a distance of less than two meters from an unprotected cliff of 1.3 meters or more.
For example, working on scaffolding during building renovations. Work at a height of more than five meters is considered steeplejack if the employee is on the very structure he is installing. For example, welding on construction beams. Industrial mountaineering can be classified as a separate category - high-altitude work using mountaineering methods of descent and ascent on a rope, as well as with special methods of belaying. Professional equipment allows industrial climbers to hang in the air for long periods of time to perform specific work.
Today, industrial mountaineering is very relevant, especially in cases where it is difficult, unprofitable or simply impossible to use lifting mechanisms, for example:
- during general construction works (facades of buildings, production buildings, etc.);
- during installation and dismantling of structures (towers and supports, advertising, ventilation, electrical, communications, scaffolding, etc.);
- in arboriculture (creating beautiful tree crowns, processing them or removing trees);
- for washing windows of high-rise buildings, clearing roofs of snow and much more.
Basic requirements for instructions for use, maintenance, periodic inspection, repair, labeling and packaging GOST R EN 365-2010 SSBT - go to document
What is the warranty period established for workwear by law?
If a warranty period has been established for the product, the buyer has the right to make claims related to defects in the product if defects are discovered during the warranty period. In the case where a warranty period of a shorter duration is established for a component product in the sales contract than for the main product, the buyer has the right make claims related to defects in a component product if they are discovered during the warranty period for the main product. If the contract establishes a warranty period for a component product that is longer than the warranty period for the main product, the buyer has the right to make claims related to defects in the product if defects in the component product were discovered during the warranty period for it, regardless of the expiration of the warranty period for the main product.4.
Why is working at height dangerous?

There is a high probability that the employee may fall down himself or something will fall on him from above. There are many reasons for this:
- improper organization of work;
- suddenly changing weather conditions;
- fatigue from heavy physical activity;
- incomplete set of personal protective equipment;
- falling of tools, piece goods from lifted containers, structural elements, etc. onto the employee.
EXAMPLE:
In the Oryol region, at ZAO Mir Roofs, workers were installing a metal covering on a hangar building. One of the roofers in safety equipment climbed to a height of about five meters using a makeshift ladder, could not resist and fell down. The worker's safety belt was not connected to the safety rope, and the safety helmet fell off his head because it was not fastened properly. The roofer died on the spot.
EXAMPLE:
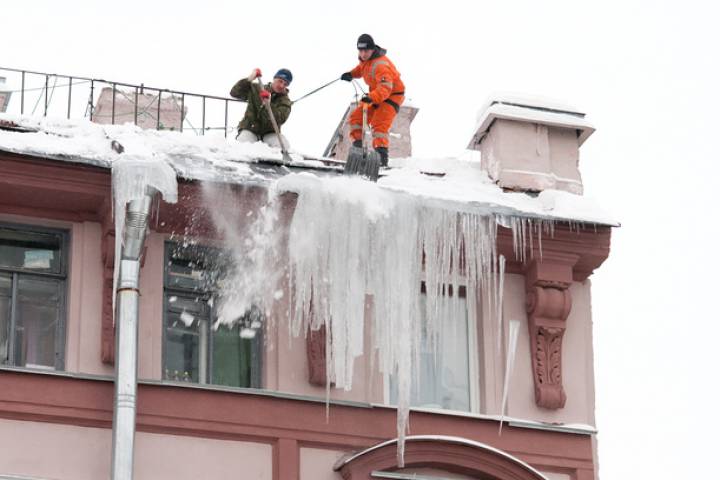
In Orenburg, employees of SK Promyshlennaya - 1 inspected the roofs. Having discovered massive icicles, one of them, without using a safety net, began dumping snow and ice onto the sidewalk adjacent to the building. The worker could not stay on the sloping metal roof and died as a result of the fall.
The risk of injury to workers due to falls is greatly reduced when modern fall protection equipment is used. According to Rosstat, one of the most common types of occupational injuries is falling from a height (more than 30% of accidents). The consequences of such falls are severe and lead to severe injuries or even death to workers. Accidents when working at height most often occur for several reasons, including:
- violation by the employer of legislation obliging workers to provide free necessary personal protective equipment, etc.;
- employee ignorance of safety rules when working at height;
- lack of awareness of the types and purposes of fall protection equipment;
- ignorance of the rules for using such protective equipment.
In order to reduce injuries when working at height, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation issued Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated March 28, 2014 No. 155n (as amended on June 17, 2015) “On approval of the Rules for labor protection when working at height.” The rules regulate work during which the employee must wear a safety harness, and work in which the use of safety harnesses is necessary. In accordance with current regulations, when restraint or work positioning is necessary, the employee must, at a minimum, use a safety harness. For work involving the risk of falling from a height, the employee is required to wear a safety harness and be secured to it with a lanyard with a shock absorber that absorbs the force of the fall. It should also be noted that, according to this Order, verification of belts and harnesses with a static load is canceled, since during such verifications the protective properties of PPE from falling from a height are significantly reduced.
It should be noted that 18% of deaths occur from falls from a height of less than 2 m, and 60% of cases of falls from height cause subsequent disability of workers. In 80% of cases, a person is seriously injured or killed due to failure to use personal protective equipment (PPE). The main reasons for not using fall protection PPE in the workplace are the following: “the models of belts/harnesses provided are inconvenient when working at heights, cause discomfort, have an incomprehensible design, and take too long to put on.” Labor safety services of enterprises must constantly work with employees, informing them about the rules for working at height, the risks of not using PPE, choosing high-quality, comfortable safety harnesses, equipment for working at height, and monitoring the use of PPE by employees in accordance with standard industry standards, working conditions and corporate standards.
Today, the Russian fall protection market offers modern, high-quality and inexpensive models with improved ergonomics and accessories for fall protection (anchor lines, carabiners, slings, locking devices, etc.) - an affordable and high-quality solution to ensure safety when working at height.
You can get acquainted with a large range of fall protection equipment by following the link to the Fire Safety online store in the “Insurance Equipment” section
Criteria and concepts when working at height
Work at height includes work when:
a) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of 1.8 m or more; b) the employee ascends a height exceeding 5 m or descends a height exceeding 5 m along a vertical ladder, the angle of inclination of which to a horizontal surface is more than 75 degrees; c) work is carried out on sites at a distance closer than 2 m from unfenced differences in height of more than 1.8 m, and also if the height of the fencing of these sites is less than 1.1 m; d) there are risks associated with a possible fall of an employee from a height of less than 1.8 m if work is carried out on machines or mechanisms, water surfaces or protruding objects.
Procedure for undergoing periodic inspections

As part of the new rules, the main document accompanying PPE, including defining the procedure for inspections, is “Instruction Paragraph 92 of the Rules” states that “PPE of workers must be taken into account and maintained in technically sound condition with the organization of their maintenance and periodic checks specified in documentation “Competent person” (these are persons with safety group 3 when working at height and who have undergone appropriate training in PPE inspection). Based on the results of inspections, based on the conclusion of a competent person, PPE is allowed for further use, otherwise it is prohibited, rejected or written off. According to paragraph “95 of the Rules”: “...Dynamic and static tests of PPE against falls from a height, with an increased load in operating organizations are not carried out...”. It turns out that from May 5, 2020, any personal protective equipment must undergo periodic testing of suitability for further use. Periodic inspections must be carried out by competent personnel who have undergone appropriate training or by organizations accredited by the manufacturer. Depending on the operating conditions and taking into account the manufacturer’s requirements, based on his conclusion, PPE is either allowed or rejected.
3. Fines
If, during an inspection of your enterprise, the Labor or other Inspectorate discovers that PPE is not certified or has not undergone periodic inspection, much less the absence of the necessary PPE, then this can lead to serious consequences.
Since 2020, fines for violations of labor safety rules and, specifically, for failure to provide workers with personal protective equipment have increased. According to Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, these violations are subject to the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of 20,000 - 30,000 rubles; for organizations 100,000 - 150,000 rubles.
Maximum service life of PPE when working at height
! The shelf life of protective equipment made of synthetic materials, subject to the rules of operation and storage, is determined in the manufacturer’s documentation, and usually does not exceed:
a) for synthetic ropes - 2 years or 400 hours of operation; b) for personal protective equipment against falls from a height that has non-metallic elements - 5 years; c) for helmets - 5 years.
Prohibition of the use of mounting and safety belts
! When using a mounting belt, in the event of a fall, there is a large load on the spine, a high risk of paralysis of the lower extremities and a high risk of falling out of the belt during a jerk.
Paragraph 104: The Rules prohibit the use of strapless safety belts when carrying out work with a possible risk of falling due to the risk of injury or death to the worker due to the shock load on the worker’s spine.
Clause 98: The Rules defines the elements of safety systems for working at height: harnesses (safety, restraining, positioning, sitting).
Belts can only be used to hold you in a working position without the risk of falling in a safe area!
Solutions for organizing safety systems using modern fall protection equipment
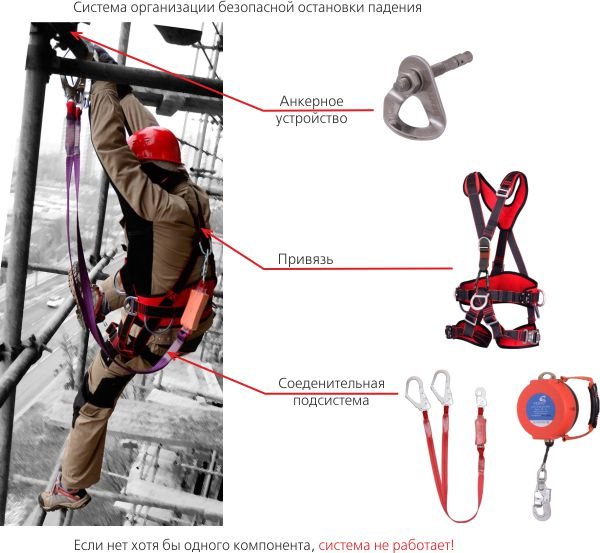
A fall protection system is a set of fall protection equipment aimed at preserving a person’s life and health in the event of a fall.
The safety system consists of:
- Anchor point.
- Connecting element (carabiner, loop) - in the online store section.
- Shock absorption systems (shock absorber).
- Intermediate connection (sling, fall arrester) - in the online store section.
- A full body harness with shoulder and hip straps or a belt - go to the online store section.

Warranty period for clothes
During the service life, the manufacturer undertakes to ensure that the product is suitable for its intended use, i.e. the product must serve while maintaining the qualities declared by the manufacturer, and in the event of significant defects in the product, the manufacturer must bear responsibility for them as provided for by law.
- For durable goods and their components, which after a certain period may become dangerous to the life and health of the consumer, as well as to the environment, or cause damage to the consumer’s property, the manufacturer is obliged to establish a service life so that the requirements for product safety can be met, i.e. e. the consumer must be informed for what period of time such a product is safe to use. The list of such goods was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 16, 1997 No. 720 (as amended.
Attention
Federal Law of December 21, 2004 N 171-FZ) Basic concepts used in this Law: consumer - a citizen who intends to order or purchase, or who orders, purchases or uses goods (work, services) EXCLUSIVELY FOR PERSONAL, FAMILY, HOME AND OTHER NEEDS NOT RELATED TO BUSINESS ACTIVITIES; (as amended by the Federal Law of December 17, 1999 N 212-FZ) manufacturer - an organization, regardless of its legal form, as well as an individual entrepreneur producing goods for sale to consumers; (as amended by the Federal Law Law of December 17, 1999 N 212-FZ) contractor - an organization, regardless of its organizational and legal form, as well as an individual entrepreneur performing work or providing services to consumers under a paid contract; (as amended.
Safety belt

The most common means of personal protection against falling from a height is a safety belt. Safety belts (SB) are divided into two main types:
- type I - strapless belts, consisting of a waist belt with a sewn-in fastening ring and a back sash;
- type II - webbing belts, consisting of a type I belt equipped with straps:
PP-II with shoulder straps (designated by the letter “D”);
- PP-II with hip straps (“E”);
- PP-II with shoulder and hip straps (“F”);
- PP-II with a saddle strap (“I”).
Safety belts are equipped with four types of fastening slings, designated by letters:
- “A”—sling made of polyamide (synthetic) tape;
- “B” - sling made of steel rope;
- “B” - sling made of polyamide rope;
- “G” – sling made of steel chain.
Product warranty
The deadlines indicated below are the deadlines for customers to make claims regarding the quality of shoes purchased from. The time limit for making claims begins to run from the date the shoes are shipped from the warehouse. For shoes for which the warranty period is not established by GOST, quality claims are accepted upon acceptance of the goods.
GOST 12.4.137-2001 - Special leather footwear for protection against oil, petroleum products, acids, alkalis, non-toxic and explosive dust.
The warranty period for wear on leather soles is 40 days, on rubber soles – 70 days from the date of sale. GOST 12.4.137-84 - Special leather footwear for protection against oil, petroleum products, acids, alkalis, non-toxic and explosive dust.
The warranty period for wear on leather soles is 40 days, on rubber soles – 70 days from the date of sale.
GOST 28507-90 — Special leather footwear for protection against mechanical influences. The warranty period is 70 days from the date of sale. GOST 5375-59 — Molded rubber boots.
The warranty period for boots is 90 days from the date of sale. GOST R 12.4.187-97 — Special leather footwear for protection against general industrial pollution.
The warranty period for leather soles is 40 days, for rubber and polyurethane soles – 70 days from the date of sale.
GOST 18724-88 – Felted coarse wool footwear.
The warranty period for felted shoes is 35 days from the date of sale. GOST 26167-2005 - Casual footwear. The warranty period for wearing shoes is 30 days from the date of sale.
GOST 12.4.072-79 — Special rubber molded boots that protect against water, petroleum oils and mechanical influences.
CONNECTING AND SHOCK ABSORBING SUBSYSTEMS FOR SAFE FALL STOPING
The task of the connecting and shock-absorbing subsystem is to safely stop a fall and minimize the severity of the consequences of stopping a fall.
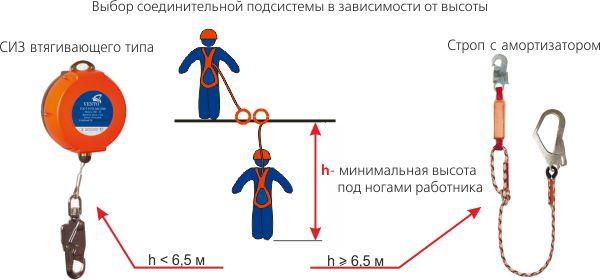
New rules and current standards require the use of 3 types of subsystems to safely stop a fall, depending on the height:
1. Using slings with shock absorbers. 2. Using a pull-in type block. 3. Use of slider-type PPE on flexible and rigid anchor lines.
Warranty period for sample workwear
Dielectric carpets 1 Dielectric carpets GOST 4997-75 Must be stored at ambient temperatures ranging from 0°C to +30°C without deformation or damage. Must be protected from direct sunlight and located at a distance of at least 1 meter from heating devices. Exposure to oils, gasoline, and other rubber-destroying substances is not allowed.
Important
It is allowed to store rugs in unheated warehouses at temperatures not lower than -25°C and transport them from -50°C to +50°C. In case of storage in conditions of negative temperatures, before putting into operation these products must be kept in packaged form at a temperature of +20°C±5°C for 24 hours. The guaranteed shelf life of carpets is 3 years from the date of manufacture.
The warranty period for carpets is 3 years from the date of their commissioning. Every 6 months check for d-el. properties.
SLIDER TYPE PPE ON FLEXIBLE AND RIGID ANCHOR LINES
Clamp on flexible anchor line
The clamp is a slider-type element on a flexible anchor line. The clamp moves freely in both directions along the flexible anchor line and is automatically fixed when the worker falls.
Purpose: for work at height when moving along vertical or inclined planes. The clamp is equipped with a shock absorber with a carabiner to reduce the load on a person when stopping a fall. Optionally equipped with a plumb line to reduce the impact of wind when working along vertical planes.
Available in lengths: 10 / 15 / 20 / 30 / 40 / 50 meters
Conditions, periods of storage and operation of PPE
In relation to a product for which an expiration date has been established, the buyer has the right to make claims related to defects in the product if they are discovered during the expiration date of the product.5. In cases where the warranty period provided for in the contract is less than two years and defects in the goods are discovered by the buyer after the expiration of the warranty period, but within two years from the date of transfer of the goods to the buyer, the seller is liable if the buyer proves that the defects in the goods arose before the transfer of the goods to the buyer or for reasons that arose up to this point. Art. 477, “Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Part Two)” dated January 26, 1996 N 14-FZ (as amended on June 29, 2015) {ConsultantPlus} Thus, it can be understood that warranty periods are established by contract or law.











