Classification of food additives
The modern classification of food additives - a numbering system (with the corresponding names of substances) - was created in the 50s of the 20th century.
It is based on assigning a unique number to each group of similar additives in order to unify, as well as simplify the perception and use of substances designed to “improve” the properties of food products. Later, after a number of changes and modifications, this classification was included in the Codex Alimentarius (Food Code adopted by the FAO/WHO International Commission) and became widespread throughout Europe, as well as some other countries. The Code is constantly updated and supplemented, and the application of classification standards is advisory in nature.
In Europe, the additive number is preceded by the letter “E”, while in Australia and New Zealand additive numbers are indicated without a prefix. In our table of food additives, “E” is written everywhere, but when searching on the page, it is better to enter only the number (this way you will definitely find the additive you need).
Food additives banned in Russia E
All food additives that are prohibited by the regulatory authorities of the Russian Federation (Rospotrebnadzor and the Russian Ministry of Health) are highlighted in red in the general list of additives “Banned in Russia (EAEU Customs Union).”
As for the mechanism for banning/permitting food additives in Russia (EAEU Customs Union), everything is quite simple here: when making decisions on permitting/prohibiting a particular additive, the Russian authorities are guided not by their own research, but by research published by JECFA (Joint Committee on Food Additives FAO/WHO)
.
This means that the laboratory of food toxicology at the well-known Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences is not directly involved in the procedure for assessing the hazard/safety of food additives.
Important !
Not all food additives harmful to health are prohibited in Russia. So don't let your guard down.
LiveInternetLiveInternet
List of harmful food additives E...
Designations of food additives starting with the letter E appeared on all food packaging in Russia after 1996. The inscription on the packaging “E124 is a safe food additive approved by ES standards” does not guarantee the safety of the additive! Firstly, this does not mean that this supplement can be consumed in any quantity.
Secondly, not everything that is permitted in Europe is permitted in Russia.
The results of new scientific research lead to the creation of some and the restriction of the consumption of other additives, even those previously considered safe.
E 100 – 199 – dyes Products with red and yellow dyes, for example, tartrazine E102, often cause food allergies. This dye is used in candies, ice cream, confectionery, and drinks.
E127 has a toxic effect, causing thyroid diseases.
E 200 – 299 – preservatives The notorious sodium nitrites and nitrates are E250 and E251. They are still used everywhere, despite the fact that they cause a variety of allergic and inflammatory reactions, headaches, liver colic, irritability and fatigue.
Substances designated by code E231 and E232 are harmful to the skin. These additives are used in the production of various sausages, meat products with a long shelf life and canned food.
Dyes and preservatives have a bad effect on the immune system and disrupt the natural intestinal microflora. And functional disorders of the intestine sometimes lead to cancer and cardiovascular pathologies. Metabolism and liver suffer. On February 22, 2005, the use of additives with the index E216 and E217 was prohibited in Russia in order to prevent the threat of mass non-infectious diseases (poisonings) of the population. Scientists speak out more harshly - these substances can provoke the occurrence of malignant tumors. Previously, these additives were used in the production of meat and confectionery products.
E 300 – 399 – antioxidants Antioxidants (they are also called antioxidants) slow down the oxidative process in fat and oil emulsions. Fats thus do not go rancid and do not change their color over time.
E311 can cause allergies and asthma attacks. An asthma attack can also be triggered by the supplements E320 and E321 (found in some fatty foods and chewing gums). E320 retains water in the body and increases cholesterol levels.
E 400 – 499 – thickeners, stabilizers Thickeners and stabilizers increase viscosity. They are almost always added to low-fat products - mayonnaise and yoghurt. The thick consistency creates the illusion of a “quality product”. May cause diseases of the digestive system.
E 500 – 599 – emulsifiers Emulsifiers create a homogeneous mixture of immiscible products, for example, water and oil. They have a negative effect on the liver and cause stomach upset. Emulsifiers E510, E513 and E527 are especially dangerous in this regard. E 600 – 699 – flavor enhancers “Miracle seasoning” allows you to save on natural meat, poultry, fish, mushrooms, and seafood. A few crushed fibers of a natural product or even its extract are added to the dish, generously flavored with an enhancer, and you get a “real” taste. The additive successfully masks the low quality of the original product, for example, old or low-grade meat. The flavor enhancer is found in almost all fish, chicken, mushroom, and soy semi-finished products, as well as in chips, crackers, sauces, various dry seasonings, bouillon cubes and dry soups. Not a single recipe in a fast food restaurant is complete without flavor enhancers. In this case, the permissible standards may be exceeded; the maximum dosage of this additive should create the illusion of a “quality product.” May cause diseases of the digestive system.
The most famous flavor enhancer is monosodium glutamate E621. There has been fierce controversy surrounding this supplement for many years. American neurophysiologist John Olney discovered in the mid-70s that monosodium glutamate can cause brain damage in rats. And Japanese scientist Hiroshi Oguro recently proved that this food additive has an adverse effect on the retina. 30% of people who frequently eat foods with monosodium glutamate complain of headaches, increased heart rate, muscle weakness, fever and bloating in the chest. This additive is especially often used in oriental cuisine, so experts have combined the described symptoms with the term “Chinese restaurant syndrome.” Monosodium glutamate is the sodium salt of the amino acid glutamine. There is a lot of it, for example, in celery root. This amino acid and its salts are involved in the transmission of impulses in the central nervous system, have a stimulating effect and are used in psychiatry. In its pure form, this substance has neither taste nor smell, but enhances the taste of any dish. To a person who often consumes monosodium glutamate, natural food seems tasteless because taste recognition receptors lose sensitivity. This is how a person becomes dependent on the “tasty seasoning.” In order not to scare away the buyer, manufacturers do not always call the E621 seasoning by its name. It is often referred to as “flavoring additive” or “taste improver.” Sometimes this formulation also hides E622 - monopotassium glutamate, which is prohibited for use in Russia. Of the 18 known flavor enhancers, 6 are allowed in Russia, but they can hardly be considered useful.
E 900 – 999 – defoamers, glazing agents, sweeteners, disintegrants. These additives prevent or reduce the formation of foam, create a shiny, smooth shell, provide the product with a sweet taste and make the dough more fluffy. Defoamers, glazing agents and disintegrants do not pose a great danger to the body.
The most serious claims are made against the sweetener aspartame. It is included in more than 6,000 products. At 30 degrees Celsius, aspartame begins to break down into methanol (methyl alcohol) and formaldehyde, which is considered a carcinogen. Chronic use of aspartame often causes headaches, ringing in the ears, allergies and depression. Another sweetener, cyclamate, has been banned in the USA, France, Great Britain and some other countries since 1969. It is believed to cause kidney failure. These sweeteners are widely used in the production of soft drinks. They increase appetite and cause thirst.
E-additives prohibited in Russia E121 - citrus red, dye E123 - red amaranth, dye E240 - formaldehyde, preservative E-additives allowed in Russia, but considered dangerous Cause the growth of malignant tumors: E103, E105, E121, E123, E125, E126, E130, E131, E143, E152, E210, E211, E213-217, E240, E330, E447. Cause diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: E221-226, E320-322, E338-341, E407, E450, E461-466. Allergens: E230, E231, E232, E239, E311-313. Causes liver and kidney diseases: E171 173, E320-322.
“Disguising” food additives that are harmful to health
Just a few years ago, most manufacturers did not hesitate to indicate food additive codes in the composition of their products. However, now bags, cans and bottles are increasingly marked with “E-shki” that are not understandable to everyone, but some foreign words that are difficult to read, let alone remember at your leisure and see how harmful/safe it is.
Therefore, when going shopping, it is highly advisable to have with you either a phone, or a phone with a camera, or at least a pencil and a piece of paper. Well, even better - a smartphone with Internet access, because then you can check the safety of any nutritional supplement on our website right in the store, “without leaving the checkout,” so to speak...
Application
Citric acid as a preservative is very popular in various industries - this is facilitated by the large number of positive characteristics that we discussed above. Let's see how the additive is used in the food industry:
- Bakery products;
- Canned vegetables and fruits;
- Confectionery;
- Soft drinks;
- Cheese products;
- Fish and fish products;
- Meat products;
- Bouillon cubes;
- Vegetable oils;
- Infant formulas and complementary foods;
- Alcoholic drinks.
We also recommend: What is citric acid made from?
Preservative E 330 is actively used in other areas - its features and properties have made it popular in the following industries:
- Pharmacological – helps improve metabolism;
- Petrochemical – reduces the acidity of the drilling fluid;
- Construction – prevents premature setting of cement;
- Cosmetic - creams, masks, lotions, deodorants whiten, disinfect and cleanse the skin, help get rid of rashes, and rejuvenate.
By the way, the element is also used in home cosmetology. It also serves as an excellent component in homemade cleaning products.
Where present
Citric acid E330 is not always added to products during production. We will introduce you to the list of products in which the component is present by default:
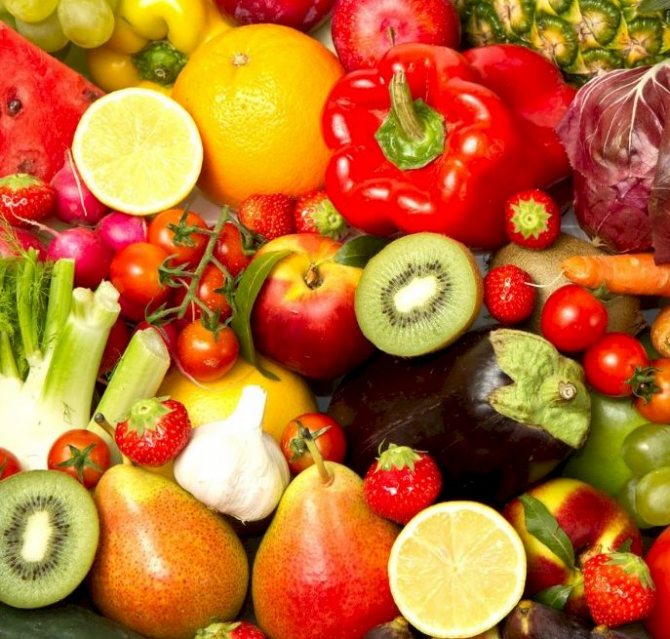

- Peaches;
- Lemons;
- Pineapples;
- Barberry;
- Strawberries and gooseberries;
- Lingonberries and rowan;
- Tomatoes;
- Apricots and pomegranates;
- Cranberry and black currant;
- Cherry and quince;
- Red pepper;
- Rose hip;
- Shag;
- Raspberry and plum.
And this is just a short list.
Interesting fact: the product is present in any living organism as an intermediate in the breakdown and synthesis of proteins and fats.
Have you studied the application areas of the component? It's time to figure out why the E330 antioxidant is harmful and useful in order to know whether it is worth using it internally and externally.
We also recommend: Palm kernel oil and palm oil: the difference