Home / Food / SanPiN
Back
Published: 10/21/2020
Reading time: 10 min
0
1019
The 2020 sanitary requirements require entrepreneurs to comply with the rules of the commercial neighborhood. The standards apply to grocery outlets, hypermarkets and catering establishments. By adhering to these provisions, the seller guarantees the consumer quality products, maintains their long-term storage and safety.
Prohibition on joint storage.
- 1 Legal framework
- 2 Basics of grocery store display
- 3 Requirements for shelf life and storage
- 4 Neighborhood according to sanitary standards
- 5 Why are sanitary standards needed?
- 6 Responsibility for violation of standards
- 7 Recommendations for entrepreneurs
Normative base
Basic documents regulating the commodity proximity of food products in trade and public catering enterprises:
- SanPiN 2.3.2.1324-03 “Hygienic requirements for shelf life and storage conditions of food products”;
- SP 2.3.6.1066-01 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for trade organizations and the circulation of food raw materials and food products in them.”
For certain types of goods, storage standards are determined by technical conditions and state standards (TU and GOST).
Attention
Monitors compliance with hygienic and sanitary-epidemiological standards, including rules of commodity proximity, Rospotrebnadzor.
Neighborhood according to sanitary standards
Food safety is based on more than just temperature and timing requirements. The main regulatory document is the rules, according to which the seller is obliged to arrange them in such a way that it does not contradict storage standards. In addition, during the period of delivery of fruits, vegetables, prepared food and meat, the entrepreneur must adhere to current laws.
Sanitary and epidemiological document No. 2.3.2.1324-03 establishes categories and provisions for ensuring the safe storage of products.
For these groups of goods, the following layout rules must be followed:
- refrigeration units;
- isolated compartments;
- shelves located at different levels;
- if there is a large area in the store - departments for selling certain goods.
The norms for the commercial proximity of food products according to SanPiN are given in the table:
Table 3.
| Class | Temperature | Note |
| Freezing | -10°С…-30°С | Constant t° support. Providing air circulation. Darkened storage compartment. |
| Canned food | 0°С…+20°С | No special conditions set |
| Dry, bulk products (tea, flour, cereals, etc.) | +12°С…+18°С | Stable temperature |
| Chilled | • meat and fish products: -1°С…-4°С; • eggs, milk: 0°С…+4°С; • butter, fat, sausage, smoked and salted fish: -2°С…-5°С; • confectionery: 0°С…+6°С; • vegetables, fruits: -1°С…+1°С | Availability of ventilation |
Placement and rules for storing food according to SanPiN
SanPiN 2.3.2.1324-03 “Hygienic requirements for shelf life and storage conditions of food products” defines the categories of food products and their storage standards. The product groups listed below should be located in separate refrigeration chambers or, in the absence of the necessary space for a large amount of equipment in the enterprise, in isolated compartments.
| Category | Storage temperature |
| Fresh milk, fermented milk products | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Pasteurized milk, sour cream, butter (chilled) | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Fresh fruits and vegetables | from 0°С to 1°С |
| Cheeses | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Chilled meat | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Chilled fish | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Chilled semi-finished meat products | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Chilled semi-finished fish products | from 0°С to 8°С |
| Frozen food | from -15°C and below |
| Dumplings | from -18°C and below |
Compatibility table
The table below shows categories and subcategories of goods that should be located in separate areas, taking into account the requirements of storage standards according to SanPin.
IMPORTANT
Products from different product groups are not allowed to be displayed or stored together.
| Product category | Storage temperature | Special storage conditions | |
| Frozen | Meat | from -10°С to -30°С | Air circulation, no light, constant temperature |
| Fish | |||
| Vegetables and fruits | |||
| Ice cream | |||
| Butter and animal fats | |||
| Canned food | Meat, fish, vegetables | from 0°С to +20°С | |
| Jams and preserves | |||
| Long-lasting confectionery products | |||
| Dry | Flour and cereals | from +12°С to +18°С | No temperature fluctuations |
| Salt, starch | |||
| Sugar | |||
| Dry spices and herbs | up to +20°С | ||
| Tea | |||
| Coffee | |||
| Chilled | Meat | from -1°С to -4°С | Ventilation |
| Fish | |||
| Eggs | from 0°С to +4°С | ||
| Milk products | |||
| Butter and edible fats | from -2°С to -5°С | ||
| Salted and smoked fish | |||
| Sausages | |||
| Cakes and pastries | from 0°C to +6°C | ||
| Some types of vegetables and fruits | from -1°С to +1°С |
How to properly store food
Each type of product has its own characteristics. Accordingly, special conditions must be created for each group. This is necessary in order to preserve their consumer properties in a marketable form and not spoil the quality characteristics of food products.
Properly storing dry and bulk products
For various types of cereals, pasta, flour, salt, sugar, etc. Rooms with high humidity are not suitable for storage. Since they are susceptible to spoilage due to dampness. Exceeding air humidity above seventy-five degrees is no longer acceptable. In addition, the warehouse for dry products should be well ventilated. The basement is not the best place for such purposes. For flour and noodles, a dry pantry with good ventilation is more suitable. The containers for such products are bags, jars (made of plastic or glass), closed with lids, which can be left on pallets or placed on shelves.
It is necessary to protect bulk goods from foreign odors, as they are very susceptible to them.
If smoked meats, coffee, spices, etc. There is no way to put it in a separate room - cover dry products with airtight packaging.
Vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and fruits can be stored under different conditions depending on their type. For the most part, a temperature of zero degrees Celsius is acceptable for storing vegetables and fruits. A little warmer is possible, colder is no longer recommended. Excess moisture in the air will lead to the onset of rotting. Too dry - it will dry out and lose its appearance. To prevent rot and mold from spreading further, it is necessary to periodically sort through the products and get rid of spoiled fruits. Good ventilation will help extend their shelf life slightly. Fruits and vegetables are stored in boxes and baskets on the floor or shelves. Potatoes are allowed to be stored in bags. Jars and barrels are intended for storing fermented products. The ideal humidity for produce such as fruits and vegetables is eighty to ninety percent. Sudden temperature changes and temperature increases of up to five degrees Celsius should not be allowed. The ideal place to store vegetables and fruits is the basement.
Rules for storing butter and cheeses
Butter and cheeses of various types are stored for the same time - fifteen days. The only difference is that the oil can be frozen, then it will last longer. And unlike cheeses, butter does not lose its quality characteristics and appearance after defrosting. These foods must be stored in containers or wrapped in bags. They are very susceptible to foreign odors, which means that proximity to greenery or other odorous goods is incompatible. Processed cheese curds are stored for no more than forty-eight hours in polymer packaging.
How to store canned food
Ordinary canned food does not cause much concern during storage. The main thing is to limit them from solar and thermal exposure. But there are also special types. Canned food, which is based on fruit, changes its color and consistency at high temperatures. And if they are too low, they release a lot of sugar. Canned food stored in tin cans without varnish changes the taste of its contents. The ideal temperature in this case is considered to be no lower than zero, but no higher than eight degrees. After opening the package, the contents of the cans must be transferred to glass containers.
How to store meat and fish products
The shelf life of meat and fish in the refrigerator at a temperature between 0-8 degrees is 5 days. If you send food to freeze, the shelf life increases significantly. The main rule is that the shelf life of a defrosted product should not exceed one day. Meat and fish semi-finished products cannot be stored for longer than 24 hours. In this case, the storage temperature varies in the same range (but should not cross the threshold of eight degrees). The only semi-finished product that can benefit from freezing is dumplings. It is recommended to sell them frozen, without prior thawing.
Rules for storing dairy products
All finished milk products should be placed on refrigeration shelves. The shelf life of fresh milk in any container (except plastic bottles) is one and a half days. If milk is boiled, it can be kept in the refrigerator for up to 72 hours, just like sour cream. The shelf life of fermented milk products is 36 hours. Milk products whose packaging has not yet been sealed are stored in accordance with the conditions and terms indicated on the packaging.
Storage of bakery finished products
Bread must be stored in special boxes (bread bins) or in enamel-coated containers that must be closed. If you plan to store the bread for a short time, you can put it in a plastic bag. But if the bread sits there for a long time, it will become damp and a moldy smell will appear. To avoid this, you need to make a small hole in the bag. Also, the bread can be wrapped in cling film, but the cut edge should be open.
Consequences of non-compliance with the commodity neighborhood
Compliance with the rules for the proximity of food products during storage according to SanPin, transportation and sale minimizes the risks of untimely spoilage of products, changes in odor, development of pathogenic flora, and deterioration in external presentation. Taking into account the individual properties of a certain group of goods, their optimal storage conditions and compatibility, the company reduces its own costs for spoiled products.
Attention
It is worth considering that unfit for consumption goods are not always visible to the naked eye, and the worst consequence of non-compliance with the rules of product proximity according to SanPin is consumers who can lose not only their health due to poisoning by a spoiled product, but also their lives.
Some fruits and vegetables need to be stored separately
It turns out that during the ripening process, vegetables and fruits release ethylene gas.
Thus, scientists advise following certain rules for storing food. One of the British supermarket chains held a campaign in which experts gave useful recommendations on how to organize food storage in such a way as not to throw it away ahead of time. Company experts suggest accustoming yourself to the principle “Throw away less, save more.” According to the author of the method, some food products should not be kept next to each other. The danger is associated with the release of a specific gas, which causes vegetables and fruits to quickly deteriorate. According to the recommendations of the organizers of the event, large amounts of ethylene gas are released by fruits such as apples, pears, apricots, bananas, kiwis, mangoes, peaches and plums. At the same time, potatoes, broccoli, lettuce, carrots, asparagus and green beans are the most sensitive vegetables to this gas.
We recommend reading: In case of an accident, where to call Rostov-on-Don
Commodity neighborhood of food products. Rules for the proximity of products in public catering and in stores
Employees of any establishment that is directly related to food products must strictly adhere to the rules of the commodity neighborhood. This will significantly extend the shelf life of products and not spoil their quality.
After all, few people will be happy to purchase a cake in a store with a pronounced smell of smoked sausage or herring. Product proximity is considered one of the most significant factors determining storage conditions. When placing goods, it is necessary to be guided by the principles of efficiency, safety and product compatibility. The rules of product proximity imply the need for careful selection of goods with identical sorption characteristics and similar storage conditions. So, it is completely unacceptable to place it next to a chilled one.
This can lead to the first one defrosting, and the second, on the contrary, freezing.
Requirements for refrigeration equipment according to SanPiN
SanPiN 2.3.2.1324-03 regulates sanitary requirements for refrigeration units in enterprises. According to the document, to control temperature and humidity conditions, all refrigeration units must be equipped with thermometers (not mercury) and psychrometers.
Individual refrigerators or compartments must be labeled according to the category of products that are stored in them.
For your information
The quantity of products to be stored cannot be greater than what the operating refrigeration equipment can accommodate.
Simultaneous storage of raw products and semi-finished products is unacceptable (frozen or chilled).
Commodity proximity of food products according to SanPiN in the refrigerator
At home, it is impossible to provide several refrigeration units for different categories of products. Modern manufacturers help housewives by equipping refrigerators with a variety of main and additional shelves and lockable containers.
Additional Information
You can store sauces, unopened packages of pasteurized milk, butter, and jam on the doors.
Eggs should be stored in separate boxes or special cells, inside the refrigerator, not on the doors, since constant temperature changes when opening/closing the door have a detrimental effect on the safety of the product. If there is dirt on the eggs, they must be washed before storing.
Dairy products must have a separate shelf. It is important that there is minimal air access into the open package.
IMPORTANT
According to SanPin, any meat must be stored separately, in an airtight container or wrapped in plastic. The most dangerous thing is the proximity of meat and dairy products, eggs or ready-made meals. Meat can be stored next to fish, but it is worth separating it from each other, for example, fish on the right, meat on the left.
In order to preserve the freshness and nutritional value of products longer, be sure to use the basic rules of product proximity and zone separate the following products from each other:
- raw products or semi-finished products are farther from ready-made dishes and products that do not require heat treatment for consumption;
- sausages and smoked meats from cheeses, fresh vegetables and fruits;
- bread from ready meals.
General storage rules
In order for catering enterprises to operate stably and without violations of SanPin norms and rules, the process of storing products must be organized at a high level:
- It is desirable to have a separate storage room for storing products subject to rapid spoilage with refrigerators and a cool temperature;
- It is desirable to have a separate pantry for storing dry foods and have a warm and dry climate with good air conditioning;
- It is desirable to have a separate pantry for storing fruits and vegetables with special conditions. The presence of shelving and a special refrigerator is only a plus.
Storerooms must be kept in order and ventilated regularly. The refrigerator for fish, herbs, meat and dairy products should be separate. If the company cannot afford such luxury, existing refrigerators are equipped with separate chambers. The main types of products must be stored separately from each other. The same rules apply to store back rooms and their counters. You cannot sell fish and meat from the same container. Storing semi-finished products and ready-made salads (for example) is also prohibited. For violation of the rules, the management of an enterprise or store is punished in accordance with the norms of Russian legislation. Namely, in Moscow, such a violation is punishable by a fine of 10 times the minimum wage. In addition, all products, including those in the refrigerator, must be stored in clean containers intended for them. The product must be marked with the name and basic packaging information.
Commodity proximity of food products according to SanPiN in public catering
At catering establishments, all products, semi-finished products and ready-made meals must be labeled according to SanPin and placed on separate shelves in refrigeration units. It is unacceptable to leave containers with any types of products uncovered. Spoons and other cutlery should not be left in prepared dishes or preparations.
For your information
When preparing dishes from different cuisines at one enterprise, according to SanPin, it is necessary to adhere to the principle of zonal separation of premises and refrigeration equipment. So, if Japanese cuisine is served in a cafe, then to prepare it you need to keep the room temperature below +16°C. Separate refrigeration chambers should also be provided for raw fish.
It is unacceptable to store good goods together with spoiled or expired ones. Products subject to write-off must be thrown away or stored in separate refrigerators.
Attention
Any foreign objects or personal belongings of enterprise employees must be kept in a specialized room. Eating is also prohibited in production areas.
In trade
Classification of goods by category:
- dry, such as flour, cereals, sugar, pasta;
- dairy and milk-fat;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- meat;
- fish;
- gastronomy;
- bread.
According to SanPin, products with the same requirements for storage conditions and similar sorption properties can be placed nearby. For the above categories of goods, separate shelves, display cases, refrigerators or freezers are provided.
IMPORTANT
The expiration dates, standards and storage conditions specified by the manufacturer on the product must be strictly observed. It is not allowed to store products with a specific odor near products that easily absorb such odors.
Refrigerators, islands and display cases should be equipped with removable shelves or be easily accessible for regular cleaning.
In grocery stores, according to SanPin, goods must be stored in supplier containers or transferred to clean containers labeled by product type.
Additional Information
If short-term storage of different categories of goods in one refrigeration unit is necessary, it is necessary to comply with the conditions of product proximity and place products on different shelves to eliminate the risk of transferring pathogenic bacteria.
Rules for storing non-food products
Storage conditions for most non-food products are the same - humidity within 65-70%, temperature from +5 to +25°C (average 10-18°C). The placement of non-food products should be no closer than 0.5-1 m from heating devices with a combination of diffused sunlight and artificial lighting (most products require protection from direct sunlight). When stacking goods, it is necessary to maintain their shape. You must follow the rules of product proximity (do not store goods together that can lead to mutual damage).
For fur products, the recommended storage temperature is from - 4°C to +5°C. For cosmetics, perfumes, water-based paints and varnishes, on the contrary, frost protection is required. Metal goods can withstand cooling to low temperatures, as well as heating, without loss of quality. Flammable, combustible or toxic (poisonous) goods (including those in aerosol packaging) require special storage conditions in separate rooms.
Hygroscopic goods (fabrics, leather, shoes, furniture) should be stored in dry rooms where air exchange and protection from microbiological damage (fungi, mold, etc.) are provided.
When storing non-food products, storage conditions are also not the same, but are determined by the specifics of individual product groups. Thus, sewing, knitwear, fur, sheepskin and fur (casing) goods and hats should be stored in dry, clean, well-ventilated areas on hangers, brackets, racks or in boxes. It is prohibited to store these goods in bulk or on the floor.
General requirements for temperature and humidity conditions for storing these goods are determined by the standards and Rules for the sale of non-food products, according to which it is recommended to store:
• garments and hats - at a temperature of 10-18 ° C and a relative air humidity of 60-70%;
• knitted goods - from 3 to 20 ° C and relative humidity 60-65%;
• fur and sheepskin products - from 5 to 25 ° C and relative humidity 60-65% In this case, outer garments should be hung on hangers - hangers in closets or on hangers, linen should be placed in stacks or in boxes on the shelves Knitted before storing products, they must be sorted by type, model, size, growth and other characteristics. To prevent contamination of these goods from dust and exposure to direct sunlight, it is recommended to cover the racks with curtains, and cover hangers and brackets in warehouses with covers made of fabric or plastic film .
Hats are stored in boxes on shelves or in boxes stacked on wooden floors.
It is recommended to store fur goods in ventilated areas at a temperature of 0-8 ° C under conditions of limited illumination. Fur clothing is recommended to be stored hanging on hangers in polymer (polyethylene) covers.
Textile goods should be stored on racks, shelves, containers in dry, clean, well-ventilated areas at a temperature of 15-18 ° C and a relative humidity of 60-65% Packaged (in boxes, bales, boxes) and unpackaged (in pieces ) goods are placed separately, while fabrics and piece textile products in boxes must be stored on shelves. To protect these goods from dust and fading, covering materials (thick fabrics, paper, synthetic films) are used or the products are enclosed in cardboard boxes, boxes, bags from film or paper.
To prevent damage to woolen fabrics during long-term storage, they must be treated with anti-mole agents.
Carpets and carpet products are stored in stacks on shelves at a distance of at least 20 cm from the floor, flattened, face up
Shoes are stored in dry, clean, well-ventilated rooms at a temperature of 15-20 ° C and a relative humidity of 50 - 70%. Shoes of all types are prohibited from being stored in bulk. Leather shoes in boxes are placed on racks at a height of no more than 8 rows, shoes without boxes (not packaged). ) - no more than 5 rows with a cardboard spacer between the rows; rubber shoes are stored on rack shelves in factory packaging or unpacked in a dimly lit room. Felting shoes are stored in factory packaging in stacks with a stacking height of no more than 1.5 m. Unpacked shoes of all types must be protected. from exposure to sunlight, felted and insulated shoes during long-term storage should also be treated with anti-mole agents.
To store jewelry made of precious metals, stores should use fireproof cabinets (safes). Artwork should be stored in dry, heated rooms, avoiding sudden temperature fluctuations.
Glass and ceramic products should be stored unpacked on shelves
Electrical household goods are stored in rooms isolated from places where acids and alkalis are stored, at an air temperature of not lower than 5 ° C and a relative humidity of not more than 65-70% in original packaging ((large-sized goods - on counters, small-sized goods - on racks) B in the same rooms, but at an air temperature of 12-18 ° C and a relative humidity of 60-70%.Large-sized television and radio products are stored in packaged form on shelves or shelves with a mandatory spacer made of wood or other material between them.
The storage of household chemicals, mineral fertilizers and plant protection products is carried out in compliance with fire safety and sanitary requirements in closed, dry, clean, well-ventilated rooms with concrete or ceramic tile floors at a temperature not lower than 9 ° C and not higher than 20 - 25 ° C with a relative air humidity of no more than 55-65%. During storage, these goods are placed separately into groups and types, taking into account their special properties.
Furniture is stored in dry, clean, ventilated rooms at a temperature not lower than 2 ° C and a relative air humidity of 45-70% using fabric covers or plastic films. Mirrors and counters are stored separately.
Perfume and cosmetic products and toilet soap should be stored on shelves and shelves in clean, well-ventilated rooms at a relative air humidity of 55-70% and air temperature:
• perfumes and cosmetics - 6-25 ° C;
• solid toilet soap - not lower than -5 ° C;
• liquid toilet soap - not lower than 5 ° C
The storage height for perfumery products should not exceed 1.5 m, for cosmetic products and toilet soap - 2 m, and these products should not be exposed to direct sunlight
Storage of dry goods is organized on racks and shelves in compliance with fire safety requirements
Timber and building materials are stored in rows, stacks, in rolls, containers, cages, bales, boxes, on racks, pallets, racks, etc. in closed and dry areas Round timber and bricks are stored under a canopy or covered.
In stock
According to SanPin, all products must be stored in warehouses in specialized containers, on racks, shelves and stockpiles located in accordance with the specifics of storing the goods. Regular wet cleaning using safe disinfectants and periodic disinsection are required.
For your information
Chilled meat carcasses or parts thereof are hung in refrigerated rooms on hooks so as not to touch each other, the floor or walls. Frozen meat and poultry are laid out on shelves.
To store baked goods, it is recommended to organize a separate chamber, while wheat and rye bread should be stored separately.
Commodity proximity of food products according to SanPiN in a refrigerator at school

Refrigeration equipment located on the premises of catering establishments serving educational institutions is subject to increased requirements.
According to SanPiN 2.4.5. 2409-08 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the organization of meals for students in general education institutions, institutions of primary and secondary vocational education” school refrigerators must be:
- modern;
- equipped with control thermometers;
- be subject to annual checks for compliance with passport characteristics;
- their number must be sufficient to comply with the rules of commodity neighborhood in the required volume.
According to SanPin, raw and prepared foods at school must be stored in separate refrigerators marked with appropriate markings. Failed refrigeration equipment should be restored as quickly as possible, and for the time required for repairs, changes should be made to the daily menu so as to fully comply with sanitary requirements when preparing dishes.
Prohibited use of products
In trade and catering establishments, the use and sale of spoiled and expired products that have changed appearance and smell, with missing expiration date labels, is prohibited.
To avoid mass poisonings and the spread of infections in public catering establishments, the use and production of:
- any meat and fish products in the absence of a veterinary certificate;
- waterfowl eggs, as well as contaminated chicken eggs;
- meat heads, trimmings, blood;
- cottage cheese from unpasteurized milk;
- production of any canned food in sealed packaging;
- drying and drying fish and mushrooms, etc.
Attention
For the preparation and sale of semi-finished products, smoked meats, canned vegetables, jellies and jellied meat, poultry and fish, pickled and salted vegetables, as well as other products dangerous from an epidemic point of view, a conclusion from the state sanitary and epidemiological service of Rospotrebnadzor is required.
Food products and food raw materials sold in trade must be accompanied by a document from the manufacturer confirming the quality and safety of the product for human health, with reference to the date and number of the permit (hygienic certificate) issued by the state sanitary and epidemiological service institutions in the prescribed manner.
The manufacturer's document for imported products, confirming their quality and safety for human health, must contain a mark from the institutions of the state sanitary and epidemiological supervision of the Russian Federation about passing the hygienic assessment of the food product in the prescribed manner.
The sale of food products and food raw materials without the availability of the specified documents confirming their quality and safety is prohibited.
Accompanying documents for particularly perishable food products must indicate the date and hour of production, storage temperature, and deadline for sale.
The quality of food products supplied to food trade enterprises is checked by commodity experts, storekeepers, financially responsible persons, managers or directors of enterprises. Acceptance of products begins with checking the accompanying documents, the quality of packaging, the compliance of food products with the accompanying documents and the labeling indicated on the container (packaging).
State sanitary and epidemiological surveillance centers carry out hygienic examination of food products only if there are special sanitary and epidemiological indications. Examination of non-standard products, as well as substandard, spoiled products, which do not require special medical competence, is carried out by commodity experts or a quality inspection.
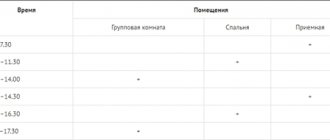
The quantity of perishable and especially perishable food products accepted should be determined by the volume of working refrigeration equipment (for storing this type of product) available at the enterprise (Fig. 3.11).
Rice. 3.11. Product storage requirements
Containers and packaging of food products must be durable, clean, dry, without foreign odors or damage to integrity.
It is prohibited to accept, store and sell perishable and especially perishable food products at food trade enterprises that are not provided with refrigeration facilities.
Storage of perishable, especially perishable food products under refrigerated conditions should be ensured not only in warehouses, but also in places of direct sale.
Each unit of packaging of highly perishable food products must be accompanied by a certificate in the established form for this type of product with a mandatory indication of the storage temperature and deadline for sale.
Certificates (labels, labels) on the supplier’s containers must be retained until the end of the food products’ sales period.
Loading of food products into warehouses, refrigerated chambers, vegetable and fruit storage facilities is carried out in batches in order to more strictly adhere to their shelf life and quality control.
Storage of food products must be carried out in accordance with current regulatory and technical documentation at the appropriate parameters of temperature, humidity and light conditions for each type of product.
Particularly perishable products should be stored at a temperature that meets the requirements of the sanitary rules “Conditions and terms of storage of particularly perishable products” SanPiN 42-123-4117-86.
When storing food products, the rules of commodity proximity and storage standards must be strictly observed. Products that have a specific odor (herring, spices, etc.) should be stored separately from products that perceive odors.
It is prohibited to store food products near water and sewer pipes, heating appliances, outside warehouses, as well as store unpackaged products directly on the floor.
It is prohibited to store raw and semi-finished products together with prepared food products, to store spoiled or questionable food products together with good quality ones, as well as to store containers, trolleys, household materials and non-food goods in food storage areas.
All food products in storage areas, cold rooms, utility rooms, etc. must be stored on racks, pallets, and shelves.
Meat is allowed for acceptance only if it has a veterinary stamp and a document certifying the inspection and conclusion of the veterinary inspection (Form 2).
It is strictly forbidden to accept meat with a veterinary certificate, but without a brand, as well as conditionally suitable meat.
Chilled meat (carcasses and half-carcasses) is stored suspended on hooks so that the carcasses do not come into contact with each other, with the walls and floor of the room.
Frozen meat can be stored on racks and shelves.
Semi-finished meat products, offal, frozen and chilled poultry must be stored in the supplier’s containers. When stacking, wooden slats must be laid between the boxes for better air circulation.
It is prohibited to accept ungutted poultry, with the exception of game, into food retail establishments.
It is prohibited to accept eggs without a veterinary certificate (form 2) for each batch of eggs on the welfare of poultry farms for salmonellosis and other zoonotic infections, as well as waterfowl eggs (duck, goose); chicken eggs that were in the incubator (mirage), eggs with cracks (“broken”), with the integrity of the shell (“tek”), contaminated chicken eggs, as well as melange.
It is prohibited to sell eggs together with other bulk products (butter, cottage cheese, cheese, sausage, etc.).
It is prohibited to wash eggs procured by consumer cooperative organizations, as well as eggs intended for long-term storage in refrigerators.
Dietary eggs are stored at temperatures from 0 to 20 °C for 7 days; dining rooms - at a temperature not higher than 20 °C - 25 days, at a temperature from 0 to 2 °C - no more than 120 days.
It is prohibited to accept and sell dairy products in contaminated glass containers, with damaged packaging, or without certificates.
It is prohibited to accept, store and sell dry infant formula in food trade enterprises that do not have proper conditions for their storage. Dry infant formula is stored at a temperature not exceeding 10 ° C and a relative air humidity of not more than 75%. The sale of infant formula must be strictly carried out within the time limits established for each type of product.
Industrially produced ice cream in food trade enterprises should be stored at a temperature no higher than -12 °C for no more than 5 days, in a retail network (trays, stalls, pavilions, kiosks) equipped with cooling means - no more than 48 hours.
Mayonnaise is stored in darkened rooms at temperatures from 3 to 18 ° C and relative air humidity of no more than 75% in accordance with the established shelf life for each type of product.
It is prohibited to store and transport mayonnaise when exposed to direct sunlight and at temperatures below 0 °C.
It is prohibited to accept and store chilled fish, hot smoked fish, culinary products and semi-finished fish products in bases and warehouses; These products must go directly to stores for sale.
Chilled fish should be stored in the container in which it was received from the supplier, the storage temperature should be -2 ° C, the shelf life in food trade enterprises is 48 hours. Frozen fish is stored in boxes stacked with slats laid between the rows of boxes in accordance with the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation.
Live fish are stored in an aquarium, in the warm season - no more than 24 hours, in the cold season - no more than 48 hours, at a temperature of 10 ° C in clean water.
Bread and bakery products are received and stored in clean, dry, well-ventilated and heated areas. It is not allowed to store bread and bakery products in bulk, close to the walls of premises, in containers on the floor without trays, as well as on racks located at a distance of less than 35 cm from the floor in utility rooms and less than 60 cm in sales areas.
In cases where signs of potato disease in bread and bakery products are detected during storage or sale, it is necessary to immediately remove such products from the sales floor and warehouse premises and take measures in accordance with the Instructions for the Prevention of Potato Bread Disease.
In order to prevent the occurrence of potato disease of bread, it is necessary to wash bread storage shelves at least once a week with warm water and soap, wipe with a 1% solution of acetic acid, and then dry.
When accepting cream confectionery products, it is prohibited to transfer cream cakes from the supplier’s trays into store containers, as well as to sell them using the self-service method.
It is strictly prohibited to accept cakes that are not individually packaged in standard cardboard boxes, as well as cakes that are not packaged in metal trays with lids (tight-fitting).
Transporting or carrying cakes and pastries on open sheets or trays is strictly prohibited.
Cream confectionery products that are not sold within the established time frame must be returned to the enterprises that manufactured them no later than 24 hours from the end of the sales period.
Products with mechanical damage or changes in appearance and shape, or with expired shelf life, in the absence of organolentic changes and the presence of foreign inclusions, are allowed to be returned for processing from the retail chain.
Soft drinks should be stored in dry, ventilated and darkened areas with a relative humidity not exceeding 75%. Sales periods and temperature conditions for storing soft drinks must comply with the requirements of current standards and technical specifications.
It is prohibited to accept and sell non-alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks that have expired, as well as drinks in bottles without labels (except for bottles with the appropriate markings on the crown caps), with damaged closures, sediments and other defects.
Before issuing canned goods for sale, the warehouse manager or merchandiser must inspect them. For each identified batch of canned food that is unsuitable for food, a report must be drawn up in accordance with the current Instructions on the procedure for accepting production and technical products and consumer goods for quality, with subsequent presentation to a commission approved by a higher organization.
Canned food deemed unfit for food must be stored in a separate room, under special records, with an exact indication of the number of rejected cans. The manager of the enterprise is responsible for the safety of rejected cans and their further use.
In cases where more than 2% of bacteriological defects (bombage) are detected in one batch of canned food, the administration of the enterprise is obliged to stop the sale of canned food in this batch, inform the manufacturer and the territorial center for sanitary and epidemiological surveillance about this in order to resolve the issue of further sale of canned food.
The question of the place and method of destruction of bomb cans is decided by the head of the enterprise in agreement with the sanitary and epidemiological service.
Storage of bulk products should be carried out in dry, clean, well-ventilated areas, not infested with barn pests, with a relative humidity of no more than 75%.
Bulk products are stored in bags in stacks on racks, at a distance of 50 cm from the walls, with a gap between stacks of at least 75 cm.
Table salt is stored separately from other products. The guaranteed shelf life of iodized salt is 6 months. from the moment of production. After the specified period, the salt is sold as regular food salt.
Fresh fruits and vegetables are stored in packaged form in special ventilated warehouses, without natural light, ensuring proper temperature and humidity conditions. The storage temperature of vegetables and fruits, depending on their type, ranges from 3 to 12 ° C with a relative air humidity of 70 to 95%.
Specialized stationary storage facilities for storing vegetables and fruits must be equipped with forced ventilation and provide the proper temperature and relative humidity for each type of product in accordance with the requirements of current regulatory and technical documentation.
Frozen vegetables and fruits are stored at a temperature of -18 °C in a relative air humidity of 90-95% for 9-12 months; in the retail chain they are stored at a temperature of -12 °C for 3-5 days.
Acceptance, storage of mushrooms and mushroom products and their sale are carried out in accordance with the current Sanitary Rules for the procurement, processing and sale of mushrooms.
In order to prevent persiniosis and pseudotuberculosis, during the storage of vegetables at bases, their quality should be periodically checked, and vegetables should be sorted and cleaned.
Responsibility for non-compliance with standards
Article 55 of Federal Law No. 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population ” provides for administrative, disciplinary and criminal liability for non-compliance with sanitary legislation.
IMPORTANT
Violation of storage rules according to SanPin at enterprises producing and trading food products entails administrative liability with the imposition of a fine, the amount of which is established in accordance with the violations identified. The responsible persons are the heads of enterprises.
For public catering establishments, there is also a penalty in the form of administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days. Rospotrebnadzor has the right to file a lawsuit demanding the complete cessation of the functioning of an organization that creates a danger of harm to consumers.