Almost every car owner has received a fine for violating traffic rules at least once. In recent years, one of the additional ways to control order on highways and roads is cameras that automatically record all facts of non-compliance with the rules.
Of course, this equipment has its advantages. However, it is not without a number of disadvantages. In particular, we are talking about fixation errors, as well as malfunctions of cameras, which leads to incorrect data. As a result, the driver who did not violate traffic rules is forced to pay a fine.
Those who are faced with this need to remember that the imposed penalty can be appealed in court or administratively. A condition for the successful completion of the case is the presence of evidence of innocence. Help and support from a qualified specialist also plays an important role.
It should be noted that to obtain legal advice it is not at all necessary to waste precious time and pay a personal visit to an expert. It is best to solve the problem remotely by seeking an online consultation. In addition to saving time, this method of communicating with a specialist will allow you to avoid high financial costs, while receiving detailed answers to all your questions.
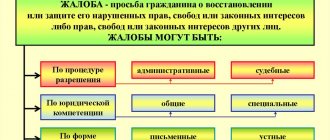
How to properly file a complaint against a decision
Every day people travel along different routes using different modes of transport. A citizen can be a pedestrian, a passenger, or a driver.
The activities of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate are aimed at ensuring road safety. By violating traffic rules, a person may be subject to administrative liability. Quite often, citizens do not agree with the decision made against them. They file a complaint.
According to Art. 30.14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the complaint must contain:
- name of the court, body to which it is filed;
- The applicant’s full name, residential address, telephone number and other contact information, if necessary and available;
- similar data about other participants;
- details of the decision being appealed;
- the person’s arguments indicating the grounds for filing a complaint;
- list of documents confirming the applicant’s position;
- signature of the applicant and date of preparation.
Note! The following must be attached to the complaint: a copy of the decision being appealed, copies of decisions, if the decision has already been appealed to other authorities.
If the complaint is filed by a representative of the applicant, then copies of documents confirming authority are attached to it. This could be a power of attorney, a lawyer's order.
The decision of the TsAFAP traffic police department of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia is made on the basis of data on the offense that were recorded by special technical means. Cameras installed on the roads provide photo and video recording. The resolution is drawn up against the owner of the car, regardless of who was driving the car at the time of the violation.
Depending on the circumstances of the case, attach all possible materials or documents confirming the arguments set forth in the complaint. For example, it is necessary to confirm that at the time the offense was recorded, it was not the owner who was driving. This could be witness testimony, video recordings from surveillance cameras located along the route, DVR recordings, photographs from the scene of an accident, a power of attorney to drive a car, a purchase and sale agreement, etc.
Is it legal for traffic police to use video cameras on houses?
Is it possible to appeal the traffic police report if you have signed it? Read here.
What is the fine for refusing a medical examination, read the link:
Possibility of appeal - deadlines
Before filing a complaint, you need to figure out whether the time for filing it has been missed. The standard deadline for sending a complaint is 10 days from the date of receipt of the punishment order. This is established in the Code of Administrative Offenses, Article 30.3.
This means that during this period you can file a reasoned objection to the fine. In this case, the beginning of the countdown of this period is not the moment of execution of the resolution, but the moment of receiving it in hand:
- the date the traffic police officer issued the decision on the road and its delivery.
- the date of receipt of the document from the post office, which was printed from a video recording camera, the so-called “letter of happiness”.
If you accidentally saw a letter with a fine in your mailbox, but did not receive it as a registered letter against signature, then in fact we can assume that you did not receive anything.
However, the appeal period has not yet begun for the 10-day countdown. This is defined by law. But in practice, the driver, due to his inexperience, can admit to receiving the order. Also, judges may not pay attention to the date of receipt of the “chain letter” and will refuse to satisfy the claim.
Read also “How and where to challenge a traffic police fine from a camera?”
If more than 10 days have passed
In this case, it is possible to restore the period, but if there are good reasons. For example, you may have gotten sick and have evidence that you were unable to complete paperwork.
You submit a petition to the court to which you are going to send the complaint with a request to restore the appeal period, providing compelling reasons. Below we will describe how to find the right court. Details on this issue can be found in the Resolutions of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of Russia.
Application methods
A complaint against the decision of the TsAFAP Traffic Police Department of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia can only be submitted in writing. Electronic submission is not currently available.
You can submit a complaint:
- addressed to the head of the video recording center of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs;
- to the district court at the place where the decision was made;
- head of the territorial traffic police department.
The structure of the traffic police departments in the constituent entities does not coincide. For example, in Moscow you can file a complaint with the district court or with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia for Moscow (address: Moscow, Sadovo-Samotechnaya St., 1).
The address and opening hours of the territorial divisions of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs for any subject of Russia can be clarified on the website of the State Traffic Inspectorate.
Important! When submitting a complaint, you do not need to take a copy of it with you. The inspector accepting the application will issue a notification coupon indicating the date and time of submission.
It is not worth filing a complaint with three authorities at the same time. The acceptance of the complaint by the court will be followed by the termination of proceedings on it by other authorities.
Terms for consideration of the application

The deadlines depend on the authority to which the complaint was filed:
- consideration by the traffic police is carried out within ten days;
- consideration by the court - within two months.
During the review process, a judge or official, regardless of the content of the complaint, checks the administrative material in full.
Watch the video. Appealing decisions on administrative offenses:
Finding the right court
There are two places that have the right to consider appeals against penalties from the traffic police:
- The head of the State Traffic Inspectorate, in which the employee who issued the order serves.
- The judicial authority at the place where the fine was imposed.
You must decide for yourself which authority to send your complaint to. But practice shows that it is better to challenge a fine in court than with the head of the State Traffic Inspectorate. In this case, the judge will most likely cancel the fine, as evidenced by court practice in 2020. Probably, the saying “one hand washes another” is very suitable in this situation, and judges consider cases related to the cancellation of fines more objectively.
In what cases can consideration be refused?
The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not provide a list of cases when consideration may be refused.
In practice, the grounds for returning a complaint without consideration are:
- the period for appeal has expired;
- the applicant did not sign the complaint. It is impossible to establish the will of a person to appeal and identify him;
- the complaint was filed by an unauthorized person. Participants in an administrative offense, their representatives, and the prosecutor have the right to file a complaint;
- the complaint does not comply with the requirements of the law, i.e. it is impossible to determine from its content how and whose rights were violated.
In all these cases, the reasons for the return are indicated.
How to appeal a violation online
According to the law, in 2020, the decision to impose a fine can be appealed in accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses, Article 30.1. This law specifies that a complaint is filed only by the person to whom the order was issued. But there is no way to appeal a fine online yet (on the portals of State Services or the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate) . This is due to the difficulty of identifying a person. An appeal is possible if you have an enhanced digital signature.
We will discuss this topic in more detail in a separate review, which will describe filing an appeal electronically.
However, a complaint can be considered electronically if you submit it in a simple way, which is discussed above. In this case, the case is considered using the Skype application. This opportunity is provided by the Code of Administrative Offenses, namely Article 29.14. But in practice, consideration of penalties on the World Wide Web is rarely carried out, and some judges refuse such a request. But you can submit such a petition by analogy with the procedure discussed above, in the event of a missed appeal period.
Why mistakes happen
The processing of road restraint materials undergoes an automated check, a manual check, and then the material goes to the inspector, who makes a decision.
Systems for recording traffic violations are complex technical systems in which errors and failures are possible. They are constantly being improved and updated.
For example, initially, video cameras recognized only the front license plate, and motorcyclists remained unpunished; currently, there are cameras on the roads that read both the front and rear license plates.
Current legislation in Part 3 of Art. 1.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation abolished the presumption of innocence for administrative offenses in the field of road traffic, when the offense itself was recorded automatically by special technical means.
Therefore, in all controversial issues, the car owner has to prove his innocence. Also, in order to adjust the system, if you receive a receipt in error, you must contact the nearest traffic police department, and if the review is refused, you must contact the court.
Features of appealing a fine in court

Many car owners prefer to pay fines, even in cases where the violation was committed by another person. This is due to the fact that citizens mistakenly believe that an attempt to prove their innocence will end in complete failure and will also entail additional financial costs.
In fact, this is not true. Practice proves that in 9 cases out of 10, an appeal against a fine is satisfied. Of course, when drawing up a sample complaint, it is necessary to comply with some requirements. In particular, we are talking about the absence of errors, rudeness, corrections and abbreviations. Although this document does not have a clearly regulated template, it must comply with the rules of business writing and the norms of the Civil Procedure Code.
The complaint sample contains the following information:
- Name of the authority to which the document is sent;
- Applicant's passport details;
- Information about the violation, including camera images;
- Arguments, arguments and evidence of the plaintiff’s innocence;
- Requirements for consideration of a complaint;
- The time of submission of the document and the personal signature of its author.
The district court deals with such claims. It is also useful to know that appealing fines does not require payment of a state fee. In fact, every citizen can go to court with a sample complaint. The main thing in this situation is to correctly and competently draw up the document itself. It must fully reflect the essence of the problem and have references to the Law.
Of course, the legislation has many nuances and pitfalls that only specialists can know about. Unfortunately, reluctance to seek help from specialists often becomes the main reason for failure in court. An incorrect interpretation of the law or an erroneous reference can play a fatal role in the process, or lead to the fact that the complaint will simply not be considered.
In cases where it was not possible to appeal the fine, or there is no evidence of the car owner’s innocence, experts strongly recommend paying the fine. Otherwise, the consequences can be extremely unpleasant. After a certain period of time, the case will be transferred to the bailiff service, and the debt will be collected forcibly.
This service has a wide range of capabilities that allow it to withhold part of the debtor’s wages, involve a citizen in public works, seize his property, and also take other actions.
Features when appealing traffic police decisions on video recording
The features include the following:
- The owner of a car fixed by special technical means is held liable;
- the presumption of innocence does not apply, the car owner is guilty until he proves otherwise;
- The law establishes the conditions for the release of a car owner from administrative liability.
Conditions in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 2.6.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation are:
- filing a complaint against the decision;
- the presence of evidence confirming that the vehicle was driven by another person. For example, a power of attorney, insurance for another person, a reported car theft, etc.
All evidence is assessed in its entirety and does not take precedence over others.
Is it possible not to pay a fine from a camera that I don’t agree with?
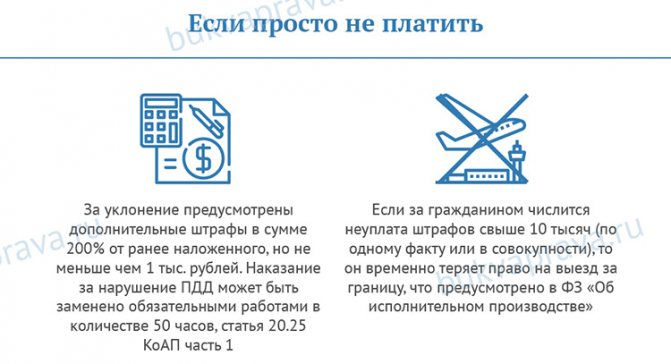
Those who decide not to take any action, simply ignore the received order, and not pay, should know that there are penalties for failure to pay penalties.
For evasion, additional monetary penalties are provided in the amount of 200% of the previously imposed, but not less than 1 thousand rubles. Punishment for violating traffic rules can be replaced by compulsory work in the amount of 50 hours, article 20.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, part 1.
This is also important to know:
How to challenge the cadastral value of real estate: apartment, land plot
If a citizen has failed to pay more than 10 thousand (on one fact or in aggregate), then he temporarily loses the right to travel abroad, which is provided for in the Federal Law “On Enforcement Proceedings”.
Therefore, it is better to understand the question of how to challenge a monetary penalty from the traffic police in a legal way than to increase the amounts.
Additionally, it is recommended to read: what is the penalty for a double continuous line.
In what cases can you appeal a traffic police decision?
In current practice, there are three groups of cases when complaints from car owners must be satisfied:
- error in processing fixation materials. This is when the photograph and reality do not coincide, for example, the decision comes to another owner of another car, the vehicle number was read incorrectly, the number in the photo is not readable, etc.;
- This also includes cases when for one recorded offense, recorded by one special technical device, several orders were issued, or, based on the results of automatic recording, a fine was issued for an offense, and the technical device used is not certified to determine it. For example, not wearing a seat belt;
- it was not the owner who was driving, and there is confirmation of this.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.