How to file a complaint to the Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation - the procedure for filing a complaint
The complaint must be submitted in writing. If the text is illegible, the application may not be accepted.
A properly drafted complaint should include:
- The name of the prosecutor's office to which you are applying.
- Institution address.
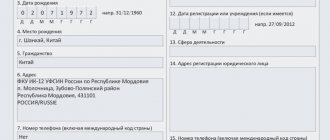
- Full name of the applicant and his contact details: address, telephone.
- A detailed description of the circumstances that forced you to contact the prosecutor's office.
- Laws that have been broken.
- Requirements.
- Date of signing.
- Applicant's signature.
Here are a few recommendations regarding the content of the complaint:
- Basically, the prosecutor's office considers applications that are written with the aim of restoring legal rights against the applicant. Other types of complaints are ignored.
- The prosecutor will not have any questions if you support your complaint with references to articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses or the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
- The prosecutor's office pays great attention to complaints directed against administrative employees.
- Make realistic demands that can be met.
- Try to express your thoughts briefly, clearly and clearly, referring only to the issue of the complaint.
How to contact Rospotrebnadzor with a complaint via the Internet
The easiest and most convenient way to convey your complaint to consumer supervision employees is to fill out an application on the website. If the request involves an unscheduled inspection of a problematic object, you will need to register on the government services portal (USIA). If an audit is not required, simply fill out the following form. Registration in such cases will not be required. In connection with the spread of Internet resources actively calling for suicide, a special website was created where you can file a corresponding complaint.
Electronic messages are submitted for processing to territorial and central offices. Persons contacting Rospotrebnadzor with a complaint via the Internet must indicate their full name and address (E-mail is sufficient, but if you want to receive a response in writing, indicate a regular one). The materials attached to the case are also submitted electronically. You should adhere to the technical restrictions established by the site administration:
- maximum message size – 2000 characters;
- size of the attached file (all major formats are supported, but it’s better to double-check) – no more than 5 MB;
- You can only add one file, so if you have several materials, they should be archived (rar and zip formats).
If the volume of the application together with the attached documents does not make it possible to fulfill these requirements, you will not be able to use the service. You will have to send a complaint to the Rospotrebnadzor office in the traditional way.
How to file a complaint with the prosecutor's office - the procedure for filing a complaint with the prosecutor's office
Complain to the prosecutor's office online via the Internet
Many prosecutor's offices have their own website. That is why they can accept the complaint electronically.
Such an appeal must have:
- Full name of the applicant.
- Address of residence and registration.
- Return email address.
- Telephone number for contact.
In fact, on the website you will find a form where you can submit a complaint. Therefore, there should be no problems with drawing up the document.
Letter of complaint to the prosecutor's office
Before sending a complaint, you should think about which prosecutor's office it is best to send it to. According to Part 1 of Article 11 of the Federal Law “On the Prosecutor’s Office of the Russian Federation,” the system is divided not only by purpose, but also by territorial effect:
- General Prosecutor's Office of the Russian Federation.
- Subjects of the Russian Federation - regional and regional.
- City and regional institutions.
But still, if you don’t know where to turn, then you can submit an appeal to any prosecutor’s office in your city. If the appeal is submitted to the wrong authority, it will be redirected to the required address of the prosecutor's office, which can, within the scope of its competence, decide and consider it. There, your complaint must be numbered, stamped and signed (as a rule, the representative who received it accepts and signs the document).
Another form of contacting the prosecutor’s office is a registered letter. You are also required to give an answer to this. You will also receive a notification that it has been accepted. Please note that the response from the prosecutor or his deputies must be reasoned, that is, explain the refusal or any other decision.
An anonymous complaint to the prosecutor's office
Anonymous complaints are not considered by the prosecutor's office. If the appeal contains information about an illegal act being prepared, then the application is sent for consideration to government agencies, which can consider it and prevent it.
Appeals
The competence, organizational forms and conditions of activity of the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation are regulated by the Federal Constitutional Law of February 26, 1997 No. 1-FKZ “On the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation”.
By the legal means specified in this Federal Constitutional Law, the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation contributes to the restoration of the violated rights of applicants who contact him, without replacing the activities of other bodies and officials.
The human rights activities of the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation complement the existing means of protecting the rights and freedoms of citizens, do not cancel or entail a revision of the competence of state bodies ensuring the protection and restoration of violated human rights and freedoms, such as, in particular, justice and prosecutorial authorities or supervisory authorities. organs.
The Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation considers complaints from applicants against decisions or actions (inaction) of state bodies, local governments, officials and civil servants, provided that the applicants have previously appealed them in court or administrative proceedings, but do not agree with the decisions taken according to their complaints.
The applicant must have the formal right to appeal to the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation, that is:
– to be a victim of a human rights violation (to be in a public relationship of “person and power”, and not to be a party to a civil contract, for example, a loan or sale), her legal representative, a lawyer, or a participant in criminal or civil proceedings, having a procedural the right to appeal a court decision that has entered into legal force;
– his rights must presumably have been violated by a decision or action (inaction) of a federal, regional or municipal government body, its official, or a court decision that has entered into legal force in a criminal or civil case (the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation has no right to interfere with the procedural the activities of independent bodies of inquiry, preliminary investigation and justice, the implementation of prosecutorial supervision, the consideration of private law disputes between citizens, with commercial and public organizations);
- preliminarily appeal a decision or action (inaction) that violates, as he believes, his rights or freedoms, in a judicial or administrative manner, attaching copies of all documents in his possession (checking reports of impending or committed crimes falls within the competence of the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation Does not apply to the Federation).
Persons in places of forced detention have the right to appeal to the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation without first appealing a decision or action (inaction) of the administration of the place of forced detention; their complaints are not subject to review by the administration of places of forced detention and are sent to the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation within 24 hours.
The Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation does not consider complaints against decisions of the chambers of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation (Federation Council and State Duma), legislative (representative) bodies of state power of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The Commissioners for Human Rights in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and their apparatuses are independent independent state bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and are not accountable to or controlled by the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation.
Whose complaints does the Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation consider?
The Commissioner for Human Rights in the Russian Federation considers complaints from citizens of the Russian Federation (regardless of their location) and foreign citizens and stateless persons located on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The procedure and time frame for consideration of a complaint by the prosecutor's office - how long does it take to consider a complaint to the prosecutor's office?
According to Article 124 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation, the prosecutor is obliged to consider the complaint within 3 days from

day of admission to the prosecutor's office. If the applicant remembered during these 3 days any other details that can be attached to the complaint, then he must report this to the office, the representative who accepted your document. Then the review period is extended to 10 days.
And appeals submitted electronically are considered within 7 days from the date of registration with the prosecutor's office.
If your complaint does not contain sufficient data to resolve the issue, the document will be returned to the complainant within 7 days. A representative of the prosecutor's office should tell you what is missing in the appeal, offer to add information, or redirect you to another authority.
Please note that complaints aimed at conducting inspections and any examinations can be considered within 1 month. The deadline must be determined by the head of the body. You must be informed about the extension of the review period.
Complaint consideration period
General requests. In accordance with the current legislation, appeals from citizens received in accordance with the general procedure are resolved within 30 days from the date of their registration, and those that do not require additional study and verification are resolved within 15 days. Extension of this period is allowed only in exceptional cases and for no more than 30 days.
Appeals in accordance with Art. 124 Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation. The period for consideration of a complaint against the actions (inaction) and decisions of the investigator, the head of the inquiry unit, the head of the inquiry body, the inquiry body, the investigator, the head of the investigative body is 3 days from the date of its receipt. In exceptional cases, when in order to verify a complaint it is necessary to request additional materials or take other measures, the complaint may be considered within 10 days, of which the applicant is notified.
The response to requests is signed:
- in district prosecutor's offices - the prosecutor or his deputies;
- in the prosecutor's office of the subject - the prosecutor, deputy prosecutors, senior assistant prosecutors, heads of department (department);
- in the General Prosecutor's Office - deputy prosecutors general, heads of departments and departments.
Prosecutor's response measures taken based on the results of consideration of complaints
Based on the results of checking the arguments of the appeals, the following decisions are made:
- on satisfaction of the appeal;
- on rejecting the arguments of the appeal;
- on clarification of the provisions of the law.
If the appeal is fully or partially satisfied, the prosecutor takes prosecutorial response measures, including:
- filing a protest against an illegal legal act or decision in an administrative case;
- submitting a proposal to eliminate violations of federal legislation;
- filing claims (applications) in court in the interests of citizens;
- initiation of cases of administrative violations;
- warns officials against violating the law.
New in blogs
DUTY
MANAGEMENT ORGANIZATION in the form
LLC Management Company "Horns and Hooves" respond to the letter
OWNER?
Letters, as you know, can be sent to the Criminal Code in several ways:
1. Via the Internet by email.
2.By personally coming to the Criminal Code and registering it and marking receipt on your COPY
3. By sending letters through Russian Post. In this case, the post office offers you to choose 3 methods of sending and delivering your letter:
3.1. A simple letter.
3.2.Registered letter with notification of receipt
3.3. Valuable letter with notification of receipt and a list of attachments.
And you have the right to decide which method of delivering a letter to the Criminal Code you choose.
The Criminal Code MUST respond to your letter. But some participants believe that the Criminal Code is obliged to respond to you also through Russian Post in the same ways (see above about 3 methods).
Or SOME claim that they are OBLIGATED TO SEND IT TO YOU by registered mail.
Maybe my opinion is NOT CORRECT.
But I take the following point of view:
The management company has the OBLIGATION to SEND you only a LETTER in a SIMPLE ENVELOPE!!!!
We have a contractual relationship with the management company.
And the main document is the MKD MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT.
If you don’t have it, then you need to decide this legally.
I have it.
And if
in the management agreement,
which is CONCLUDED between the OWNERS and the Management Company, there are clauses reflecting and indicating that the Management Company, at your request stated in your letter (complaint, Claim, request), is OBLIGED to send you a letter via Russian Post by REGISTERED or VALUABLE letter,
then she will do so. !!!!!!
But on the CONDITION that
1. THIS IS SPECIFIED IN THE MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT
1.1. This was adopted at the OSS and one of the points of the OSS decision and the protocol is the POINT on increasing the CONDITIONS OF THE PRICE OF THE MANAGEMENT AGREEMENT (ORDER OF THE PRICE OF THE MANAGEMENT CONTRACT) by the NTH amount of the increase in the SiRZH in connection with the FULFILLMENT of the management company's wishes of the owners for sending by REGISTERED or VALUABLE letters.
1.2. In addition, remember that these are not EMPLOYEES, businessmen work for the management company, therefore, almost every senior representative of the management company knows what % is in MANAGEMENT of a management agreement. And in the terms of the contract it is less than 10% of the AMOUNT of the SIR and is not included. Therefore, do not forget that the Criminal Code for this article will also require that you pay at least 10% to the board and to YOUR wishes according to letters, in monetary terms and in terms of 1 square meter of the total area of your apartment.
Excerpts from the Internet:
First of all, the procedure for requests and the deadlines for responding to requests to the Management Company must be specified in the management agreement. It defines the obligation to respond to requests and the procedure for considering customer requests. But the management agreement should not infringe on the rights of the consumer (Article 16 “Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights”). If the terms of a management agreement violate established laws or other legal acts of the Russian Federation, then such agreements are declared invalid.
Also, the procedure for considering applications is defined in the Information Disclosure Standard for organizations operating in the field of management of apartment buildings, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 23, 2010 N 731 (clauses 20 and 21):
Requests received electronically, as well as written requests received and copies of responses to consumers are stored by the management organization on electronic and paper media, respectively, for at least 5 years.
Providing information upon a written request is carried out within 20 days from the date of its receipt (SEE CHANGES ABOUT 10 WORKING DAYS!! - addition from clause 21 of the RF PP No. 731) by sending (in writing) to the address of the owner of the postal item or issuing the requested information personally to the consumer at the location of the management organization.
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 23, 2010 N 731
“On approval of the standard for information disclosure by organizations operating in the field of management of apartment buildings”
GARANT system: https://base.garant.ru/12179104/#friends#ixzz3rc55uaos
20. Requests received electronically, as well as written requests received and copies of responses to consumers are stored by the management organization, partnership and cooperative, respectively, on electronic and paper media for at least 5 years.
Information about changes:
By Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 27, 2014 N 988, paragraph 21 of this Standard is set out in a new edition, which comes into force on December 1, 2014.
21. The provision of information upon written request is carried out by the management organization, partnership or cooperative within 10 working days from the date of its receipt by sending a postal item to the consumer, or issuing the requested information personally to the consumer at the location of the management organization, management bodies of the partnership or cooperative, or sending information to the consumer’s email address if such an address is specified in the request.
22. A written request received by the management organization is subject to registration on the day of its receipt, assigning it a registration number and affixing the stamp of the corresponding management organization.
23. The written request signed by the consumer indicates the management organization, partnership or cooperative to which the request is sent, the surname, first name and patronymic (name of the legal entity) of the consumer, the essence of the application is stated, and also if a written request is sent to the management organization, the postal address is indicated the address to which the response should be sent, and the method of obtaining the information (by mail or delivery in person to the consumer).
In addition, PLEASE answer the QUESTION
And what does Federal Law No. 59-FZ of May 2, 2006 “On the procedure for considering appeals from citizens of the Russian Federation” (with amendments and additions) have to do with a commercial structure in the form of LLC Management Company “Horns and Hooves”?
GARANT system: https://base.garant.ru/12146661/#ixzz3rc6lZvxC
Article 1. Scope of application of this Federal Law
GUARANTEE:
By Decree of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of July 18, 2012 N 19-P, the interrelated provisions of Part 1 of Article 1 and Article 3 of this Federal Law:
- are recognized as not contradicting the Constitution of the Russian Federation, since - in their constitutional and legal meaning in the system of current legal regulation - they in themselves do not prevent the introduction by laws of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation in order to protect the constitutional right of citizens to apply for provisions that complement the federal guarantees of this right and do not imply imposing new responsibilities (restrictions on rights) on individuals and legal entities;
- are recognized as not complying with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, its Articles 19 (Part 1), 30, 33, 45, 55 (Part 3) and 76, to the extent that they - due to the uncertainty of the normative content, giving rise in practice to their ambiguous interpretation and , accordingly, the possibility of arbitrary application - prevent the extension of the provisions of this Federal Law to relations related to the consideration by state authorities and local government bodies of appeals from associations of citizens, including legal entities, as well as the consideration of appeals by state and municipal institutions and other organizations performing publicly significant functions , including the introduction by law of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation of provisions on the possibility of considering applications by such institutions and organizations.
Pending the entry into force of a new legal regulation, the provisions of Part 1 of Article 1 and Article 3 of this Federal Law must be applied based on the requirements of Articles 19 (Part 1), 33, 45, 72 (clause “b” of Part 1) and 76 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and legal positions of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation based on them, expressed in the above-mentioned Resolution
1. This Federal Law regulates legal relations related to the exercise by a citizen of the Russian Federation (hereinafter also referred to as a citizen) of the right assigned to him by the Constitution of the Russian Federation to appeal to state bodies and local government bodies, and also establishes the procedure for considering citizens' appeals by state bodies and local government bodies and officials.
2. The procedure for considering citizens' appeals established by this Federal Law applies to all citizens' appeals, with the exception of appeals that are subject to consideration in the manner established by federal constitutional laws and other federal laws.
3. The procedure for considering appeals from citizens established by this Federal Law applies to legal relations related to the consideration of appeals from foreign citizens and stateless persons, except for cases established by an international treaty of the Russian Federation or federal law.
Information about changes:
Federal Law No. 80-FZ of May 7, 2013 supplemented Article 1 of this Federal Law with Part 4
4. The procedure established by this Federal Law for the consideration of citizens’ appeals by state bodies, local self-government bodies and officials applies to legal relations associated with the consideration by these bodies, officials of appeals from citizens’ associations, including legal entities, as well as to legal relations associated with the consideration of appeals citizens, associations of citizens, including legal entities, performing publicly significant functions by state and municipal institutions, other organizations and their officials.
GUARANTEE:
See comments to Article 1 of this Federal Law
Now, find the words about LLC (LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY) in this Federal Law and then you will be happy and the Farts in the form of LLC Management Company “Horns and Hooves” will answer you on the basis of this LAW and then you can say about those who refer to the Federal Law in their letters No. -59, that YOU CONSIDER POOK as a structure of OFFICIALS.
YES, don’t forget about the CONSUMER RIGHTS PROTECTION LAW!!!. See what the deadlines for responses to your requests are, but on the condition that in your letter several times you CALL yourself a consumer, and not an owner, and indicate the ZPP!!!
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the deadlines may be provided for by law or contract; if you are in a contractual relationship with a private organization as a consumer, then the period for consideration of the claim by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is 10 days.
In other cases, the parties may establish terms for consideration of claims in the AGREEMENT.
If the terms are not established by the contract, then the concept of a reasonable period is applied (that is, sometimes, analogous to the Federal Law, 30 days, but SPECIFIED IN THE CONTRACT)).
THEY ARE A COMMERCIAL ORGANIZATION!!!!
RIP!!!!
Conclusion:
It’s up to you to decide how to write and how to think about written answers from the Criminal Code to owners (consumers) or according to Federal Law No. 731 or according to ANALOGY with Federal No. No. 59!!!!!!
But we must still remember that the Criminal Code can also put spokes in wheels. You tell her about Federal Law 731 and ZPPP (February 7, 1992 N 2300-1), and they tell you about Federal Law -59, or Options for FOOTBALLS, or CARUSELS.
Therefore, I think that in the letter addressed to the head of the management company, you should also make a note stating that you want to receive the letter PERSONALLY at the management company after communicating with you by phone and although you indicated the NUMBER in the header of the letter, do not be lazy, DUPLICATE.
What cases are heard in the European Court of Human Rights?
The European Court of Justice (International Court of Human Rights), based in Strasbourg, is an effective international organization whose jurisdiction includes the consideration of complaints received from individuals, groups of individuals, or non-governmental organizations claiming that human rights set out in the Convention have been violated .
In what cases are complaints accepted by the Court of Human Rights?
The Convention is represented by an international treaty confirming the assumed obligations of the participating states, as well as their strict implementation. The human rights established in the Convention, which are protected by the Court, include: – the right to judicial review in criminal and civil cases; – the right to nominate one’s own candidacy in elections and the right to participate in them; – the right to freedom of religion, thought and conscience; – the right to freedom of opinion; – the right to life and personal integrity; – the right to freedom to dispose of property and the right to property; – the right to freedom of association and other organizations.
The rights protected by the Convention are set out in some of the Protocols, as well as in the Convention itself.
What cases are heard by the Strasbourg Court?
The European Court can competently begin to consider the case only after filing a complaint. The Strasbourg Court can consider two types of complaints: an individual complaint (an individual against a State party to the Convention) and an interstate complaint (one country against another).
The Court considers only complaints that relate directly to violations of the rights set out in the Convention and the Protocols. The court is not an appellate or cassation authority in relation to a national court and is not authorized to change or cancel decisions made by state authorities. In addition, this organization is not authorized to directly interfere with the work of the authority about whose work the complaint was received.
The Court considers only properly formulated complaints directed against States Parties that have ratified the Convention or the Protocols. However, the Court does not have the right to accept for consideration those complaints that have any relation to events that occurred before ratification.
Before filing a complaint with the European Court of Human Rights, it is necessary to make sure that a public organization (judicial, executive, legislative, etc.) of a certain state is responsible for the events that caused the violation of human rights.
In accordance with Article 35, paragraph 1 of the Convention currently in force, a complaint can be accepted by the Court for consideration only after all available domestic remedies have been applied. In this case, the document can be submitted to the Court no later than six months, starting from the moment the final decision is made. Complaints that do not meet the established eligibility requirements will not be considered.
For example, before sending a complaint to the European Court of Human Rights, you must first contact the highest court with jurisdiction to consider your case. But, if this document is submitted for a court decision (for example, for a conviction), and also if the case is under appeal, there is no need for additional appeal to the appropriate authorities.
Moreover, the first written appeal to the European Court of Human Rights (even in a short form) is the basis for interrupting the six-month period. The letter must clearly state the subject of the complaint. It may also be a completed complaint form. A simple letter merely asking for the required information is not sufficient and cannot serve as a basis for suspending the six-month period.
One of the important conditions that directly influences the Court’s decision to consider the complaint is the fact that all government authorities have been used through which the violation of rights could be eliminated. Or providing the Court with convincing evidence that in your case, the use of such legal remedies would be futile and ineffective.
Using state legal remedies requires compliance with all procedural norms and, most importantly, compliance with the deadlines prescribed by law. For example, if a complaint is rejected because it was received in violation of the procedure, or late, the likelihood of its consideration by the Court is sharply reduced.
But at the same time, in cases where the object of the complaint is a court verdict, then before applying to the European Court of Human Rights, it is not necessary to go through the judicial appeal procedure. In addition, in this case there is also no need to apply for an amnesty or pardon.
Recommendations for filling out a complaint form to the European Court of Human Rights
When filing a complaint with the European Court of Human Rights, it is important to remember that petitions to the executive or legislative authorities are not part of the legal remedies that can be effectively used for appeal.
It should be especially noted that more than 90% of complaints received by the Court are rejected due to non-compliance with the conditions presented above.
Procedure for considering complaints filed with the court
When filing an application with the court, there are three main documents that govern the activities of the parties. The first of them is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The second is the CAS of the Russian Federation. It regulates the status of the application filed, the obligations and rights of the party. The third is the agro-industrial complex. Its rules govern the filing and consideration of a claim.
For individuals, the main document is the CAS, and for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities the main document is the APC. According to clause 2, part 2, art. 1 of the Code of Arbitration Code of the Russian Federation, courts are engaged in the consideration and resolution of administrative cases on the restoration of violated rights, interests and freedoms of citizens and organizations.
In addition, they are engaged in challenging decisions of state authorities, other government bodies, military departments, local governments, officials and civil servants.
In order for individuals, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs to file an application with the court with a request to challenge a decision or action taken by state authorities, local authorities, and other organizations related to municipal or state structures, there is Part 1 of Art. 218 CAS RF. Based on the same Article 5, an application is submitted according to the rules of jurisdiction.
Complaints are processed in the following order. The court of first instance in considering applications is the district court. If the defendant in the application indicates a government authority or any other of the above-mentioned organizations, then the application is submitted to the court at the location of this institution.
If the defendant is an employee of one of the authorities or another municipal institution, then it is necessary to go to court at the location of the organization. Based on Part 3 of Art. 24, the application can be submitted at the place of residence of the administrative plaintiff, if there is one.
If the administrative plaintiff is an enterprise, then the application is submitted at the location of the enterprise.
If acts drawn up by tax authorities are challenged, they are appealed in the same manner in the arbitration court.
In order to begin legal proceedings, you must file a statement of claim. Such a statement can be written in several forms, depending on the essence of the case under consideration:
- statement on economic disputes and other matters;
- statements about cases arising from administrative and other public legal relations;
- application for bankruptcy;
- application for special proceedings.
When applying to the arbitration court of cassation and appeal, it is necessary to file not an application, but a complaint. Issues regarding economic and entrepreneurial activities are considered by the arbitration court according to the general rules for claim proceedings.
Individuals and legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs, have the right to apply to the arbitration court with a request to declare non-normative acts of tax authorities invalid or with a request to resolve the issue of unlawful actions of the tax authority or the adoption of an unlawful decision.
The reasons for such appeals may be the plaintiff’s opinion that the above does not comply with the legislation of the country in general or a regulatory act in particular. Or if the victims believe that their interests and rights in the area of their activities have been violated.
The plaintiff may file a claim for the unlawful assignment of duties to them under this document. Or because tax authorities create obstacles for them to conduct business activities.